I loaded aloog rock into asingshat. The Sline Shot works like caspring witha Spcing constant of 300n/M. I pulled Meters and released from rest, what is the Douer the Slingshot release the rock in watts, rockk is pulled back 0,4ab delners tothe rocke at Ne moment eeu
I loaded aloog rock into asingshat. The Sline Shot works like caspring witha Spcing constant of 300n/M. I pulled Meters and released from rest, what is the Douer the Slingshot release the rock in watts, rockk is pulled back 0,4ab delners tothe rocke at Ne moment eeu
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question
Is it around 36 ?
![**Transcription for Educational Website:**
---
I loaded a 1000 g rock into a slingshot. The slingshot works like a spring with a spring constant of 300 N/m. The rock is pulled back 0.496 meters and released from rest. What is the power the slingshot delivers to the rock at the moment just before release in watts?
**Power = Force x Velocity or Energy/Time?**
\[0.496 \times\]
---
**Explanation:**
In this exercise, a 1000 g rock is used to demonstrate the principles of physics involving springs and power. The slingshot operates similarly to a spring, described by Hooke's Law, which states that the force exerted by a spring is proportional to its extension. The constant of proportionality is known as the spring constant (300 N/m in this case).
The problem asks to find the power delivered to the rock. Power can be calculated using the formula:
\[ \text{Power} = \text{Force} \times \text{Velocity} \]
or as the rate of energy transfer:
\[ \text{Power} = \frac{\text{Energy}}{\text{Time}} \]
To solve this, one would need to calculate the force exerted by the slingshot at the point of release and understand how energy transforms into kinetic energy as the rock is released. Here, the extension of the slingshot is given as 0.496 meters, which should be used in the calculations.
The image does not contain graphs or diagrams, just text with placeholders for further calculations.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F9db44b9e-2fd8-4c74-a9ca-20a6dfd76b06%2Fb2017956-31e1-45c8-8b51-bbb21818501d%2Failz1ti.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription for Educational Website:**
---
I loaded a 1000 g rock into a slingshot. The slingshot works like a spring with a spring constant of 300 N/m. The rock is pulled back 0.496 meters and released from rest. What is the power the slingshot delivers to the rock at the moment just before release in watts?
**Power = Force x Velocity or Energy/Time?**
\[0.496 \times\]
---
**Explanation:**
In this exercise, a 1000 g rock is used to demonstrate the principles of physics involving springs and power. The slingshot operates similarly to a spring, described by Hooke's Law, which states that the force exerted by a spring is proportional to its extension. The constant of proportionality is known as the spring constant (300 N/m in this case).
The problem asks to find the power delivered to the rock. Power can be calculated using the formula:
\[ \text{Power} = \text{Force} \times \text{Velocity} \]
or as the rate of energy transfer:
\[ \text{Power} = \frac{\text{Energy}}{\text{Time}} \]
To solve this, one would need to calculate the force exerted by the slingshot at the point of release and understand how energy transforms into kinetic energy as the rock is released. Here, the extension of the slingshot is given as 0.496 meters, which should be used in the calculations.
The image does not contain graphs or diagrams, just text with placeholders for further calculations.
Expert Solution
Step 1
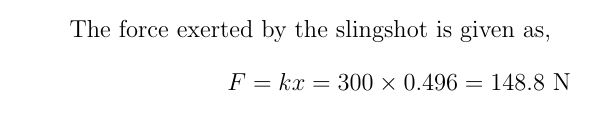
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON