Atomic Structure
The basic structure of an atom is defined as the component-level of atomic structure of an atom. Precisely speaking an atom consists of three major subatomic particles which are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Many theories have been stated for explaining the structure of an atom.
Shape of the D Orbital
Shapes of orbitals are an approximate representation of boundaries in space for finding electrons occupied in that respective orbital. D orbitals are known to have a clover leaf shape or dumbbell inside where electrons can be found.
How would I determine the element given the following information:
1/85 mol of this atom would contain 1 mol of protons?
All atoms in periodic table get specified by their particular protons/electrons as well as neutrons number. Each atom carries fixed electrons/protons as well as neutrons number which remains fixed. The atomic number always defines several chemical characteristics carried by these atoms.
Given:
The number of protons is 1/85 mol.
The relation between moles and atoms is shown below.
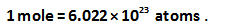
Since it is given that 1/85 moles of the atom (element) possess 1 mole of protons.
The conversion of moles of element into atoms is shown below.

Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images









