Discussion Questions* 1. Angela is now going to evaluate a new salt process delivery sys- tem and wants to know if the upper and lower control limits at 3 standard deviations for the new system will meet the upper and lower control specifications noted above. The data (in percents) from the initial trial samples are: Sample 1: 1.98, 2.11, 2.15, 2.06 Sample 2: 1.99, 2.0, 2.08, 1.99 Sample 3: 2.20, 2.10. 2.20, 2.05 Sample 4: 2.18, 2.01, 2.23, 1.98 Sample 5: 2.01, 2.08, 2.14, 2.16 Provide the report to Angela. 2. What are the advantage and disadvantages of Frito-Lay drivers stocking their customers' shelves? 3. Why is quality a critical function at Frito-Lay?
Discussion Questions* 1. Angela is now going to evaluate a new salt process delivery sys- tem and wants to know if the upper and lower control limits at 3 standard deviations for the new system will meet the upper and lower control specifications noted above. The data (in percents) from the initial trial samples are: Sample 1: 1.98, 2.11, 2.15, 2.06 Sample 2: 1.99, 2.0, 2.08, 1.99 Sample 3: 2.20, 2.10. 2.20, 2.05 Sample 4: 2.18, 2.01, 2.23, 1.98 Sample 5: 2.01, 2.08, 2.14, 2.16 Provide the report to Angela. 2. What are the advantage and disadvantages of Frito-Lay drivers stocking their customers' shelves? 3. Why is quality a critical function at Frito-Lay?
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter2: Introduction To Spreadsheet Modeling
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20P: Julie James is opening a lemonade stand. She believes the fixed cost per week of running the stand...
Related questions
Question
Hello,
I am having issues answering the homework problems.
I am supposed to find the Upper Control Limit (UCL), Lower Control Limit (LCL), and mean. and from that create a x-bar chart and r chart, but the class work is very different from the homework. Could you please help me solve the questions.

Transcribed Image Text:Quality Control Case Study
>Frito-Lay's Quality-Controlled Potato Chips
Frito-Lay, the multi-billion-dollar snack food giant, produces bil-
lions of pounds of product every year at its dozens of U.S. and
Canadian plants. From the farming of potatoes-in Florida, North
Carolina, and Michigan-to factory and to retail stores, the ingredi-
ents and final product of Lay's chips, for example, are inspected at
least 11 times: in the field, before unloading at the plant, after wash-
ing and peeling, at the sizing station, at the fryer, after seasoning,
when bagged (for weight), at carton filling, in the warehouse, and as
they are placed on the store shelf by Frito-Lay personnel. Similar
inspections take place for its other famous products, including
Cheetos, Fritos, Ruffles, and Tostitos.
In addition to these employee inspections, the firm uses propri-
etary vision systems to look for defective potato chips. Chips are
pulled off the high-speed line and checked twice if the vision sys-
tem senses them to be too brown.
The company follows the very strict standards of the American
Institute of Baking (AIB), standards that are much tougher than
those of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Two unannounced
AIB site visits per year keep Frito-Lay's plants on their toes. Scores,
consistently in the “excellent" range, are posted, and every employee
knows exactly how the plant is doing.
There are two key metrics in Frito-Lay's continuous improve-
ment quality program: (1) total customer complaints (measured on a
complaints per million bag basis) and (2) hourly or daily statistical
process control scores (for oil, moisture, seasoning, and salt con-
tent, for chip thickness, for fryer temperature, and for weight).
In the Florida plant, Angela McCormack, who holds engineer-
ing and MBA degrees, oversees a 15-member quality assurance
staff. They watch all aspects of quality, including training
employees on the factory floor, monitoring automated pro-
cessing equipment, and developing and updating statistical
process control (SPC) charts. The upper and lower control limits
for one check point, salt content in Lay's chips, are 2.22% and
1.98%, respectively.

Transcribed Image Text:Control Chart Factors
Mean Factor Upper Range
A2
Lower Range
D3
Sample Size
DA
2
1.880
3.268
3
1.023
2.574
4
.729
2.282
5
.577
2.115
.483
2.004
7
.419
1.924
0.076
8
.373
1.864
0.136
9
.337
1.816
0.184
10
.308
1.777
0.223
12
.266
1.716
0.284

Transcribed Image Text:Discussion Questions*
1. Angela is now going to evaluate a new salt process delivery sys-
tem and wants to know if the upper and lower control limits at
3 standard deviations for the new system will meet the upper and
lower control specifications noted above.
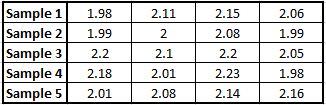
The data (in percents) from the initial trial samples are:
Sample 1: 1.98, 2.11, 2.15, 2.06
Sample 2: 1.99, 2.0, 2.08, 1.99
Sample 3: 2.20, 2.10. 2.20, 2.05
Sample 4: 2.18, 2.01, 2.23, 1.98
Sample 5: 2.01, 2.08, 2.14, 2.16
Provide the report to Angela.
2. What are the advantage and disadvantages of Frito-Lay drivers
stocking their customers' shelves?
3. Why is quality a critical function at Frito-Lay?
Source: Professors Barry Render, Rollins Coilege; Jay Heizer, Texas
Lutheran University; and Beverly Amer, Northern Arizona University.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given-
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
How do you calculate 2.282 and 0 for the UCL and LCL
Solution
Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781285869681
Author:
Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781478623069
Author:
Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen
Publisher:
Waveland Press, Inc.