How do shape and symmetry influence the polarity of a molecule? cite specific examples. 2. Classify each covalent molecule as polar or nonpolar.
Types of Chemical Bonds
The attractive force which has the ability of holding various constituent elements like atoms, ions, molecules, etc. together in different chemical species is termed as a chemical bond. Chemical compounds are dependent on the strength of chemical bonds between its constituents. Stronger the chemical bond, more will be the stability in the chemical compounds. Hence, it can be said that bonding defines the stability of chemical compounds.
Polarizability In Organic Chemistry
Polarizability refers to the ability of an atom/molecule to distort the electron cloud of neighboring species towards itself and the process of distortion of electron cloud is known as polarization.
Coordinate Covalent Bonds
A coordinate covalent bond is also known as a dative bond, which is a type of covalent bond. It is formed between two atoms, where the two electrons required to form the bond come from the same atom resulting in a semi-polar bond. The study of coordinate covalent bond or dative bond is important to know about the special type of bonding that leads to different properties. Since covalent compounds are non-polar whereas coordinate bonds results always in polar compounds due to charge separation.


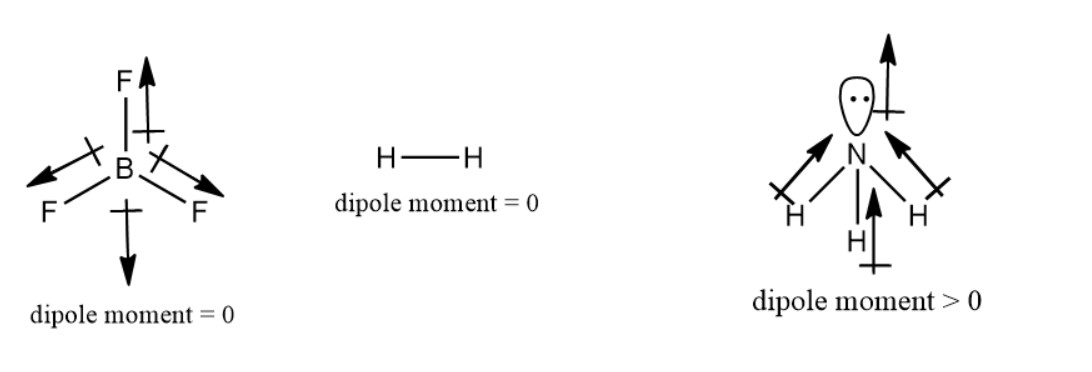
1) Shape and symmetry has a great role in determining the polarity of a molecule. A complete symmetric molecule has no polarity. Dipole moment = charge x distance between two poles
= q x d
A complete symmetric molecule has same value in all the directions. Therefore they cancel out each other and net dipole moment value becomes zero. So it is non polar. e.g. BF3 molecule. In BF3 molecule, has a structure of trigonal planar. The dipole moment vector of three F atoms cancel out each other. Therefore BF3 is non polar even though the three B-F bonds have polarity towards F -atom (electronegative atom).
Again, symmetric molecule H2 has linear shape. For the same reason it is also non polar.
The molecule which is polar must be non-symmetrical. e.g. NH3 (ammonia). In NH3 molecule N-atom is sp3 hybridized having tetrahedral geometry according to hybridization. But the shape of ammonia is trigonal pyramidal due to presence of lone pair over N-atom. As NH3 is non-symmetric, therefore net dipole moment 0. So it is polar.
The polarity of the following molecules is shown in this image.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









