Homicide and suicide are both intentional means of ending a life. However, the reason for committing a homicide is different from that for suicide and we might expect homicide and suicide rates to be uncorrelated. On the other hand, both can involve some degree of violence, so perhaps we might expect some level of correlation in the rates. The data from 2008–2011 for 26 counties in Ohio are shown in the table. Rates are per 100,000 people. (a) Make a scatterplot that shows how suicide rate can be predicted from homicide rate. There is a weak linear relationship, with correlation ?=0.17. Each of the scatterplots in the choices has a relationship fitted to the plot. Select the plot that corresponds with the correlation of 0.17. (b) Find the least‑squares regression line for predicting suicide rate from homicide rate, ?+?×(homicide). (Enter your answers rounded to three decimal places.) a = b = Explain in words what the slope of the regression line tells us. A) The slope means that for every additional suicide (per 100,000 people), there is an average increase of 0.1260 homicide (per 100,000 people) in these Ohio counties.
Homicide and suicide are both intentional means of ending a life. However, the reason for committing a homicide is different from that for suicide and we might expect homicide and suicide rates to be uncorrelated. On the other hand, both can involve some degree of violence, so perhaps we might expect some level of
(a) Make a
Each of the scatterplots in the choices has a relationship fitted to the plot. Select the plot that corresponds with the correlation of 0.17.
(b) Find the least‑squares regression line for predicting suicide rate from homicide rate, ?+?×(homicide). (Enter your answers rounded to three decimal places.)
a =
b =
Explain in words what the slope of the regression line tells us.
scatterplot is given below 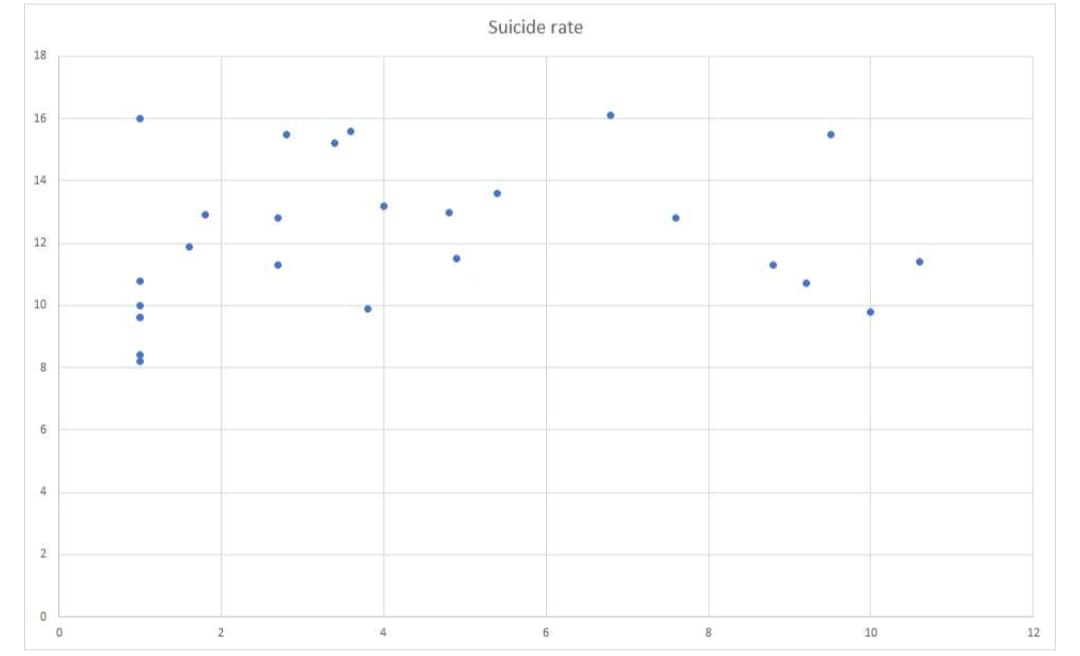
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 2 images









