Catalysis and Enzymatic Reactions
Catalysis is the kind of chemical reaction in which the rate (speed) of a reaction is enhanced by the catalyst which is not consumed during the process of reaction and afterward it is removed when the catalyst is not used to make up the impurity in the product. The enzymatic reaction is the reaction that is catalyzed via enzymes.
Lock And Key Model
The lock-and-key model is used to describe the catalytic enzyme activity, based on the interaction between enzyme and substrate. This model considers the lock as an enzyme and the key as a substrate to explain this model. The concept of how a unique distinct key only can have the access to open a particular lock resembles how the specific substrate can only fit into the particular active site of the enzyme. This is significant in understanding the intermolecular interaction between proteins and plays a vital role in drug interaction.
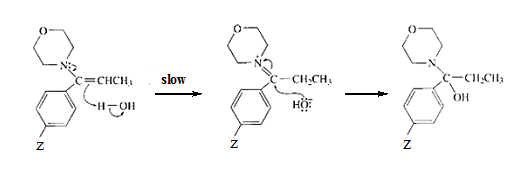
To solve this problem, you need to read the description of the Hammett s, r treatment given in Chapter 15, Problem 92. When the rate constants for the hydrolysis of several morpholine enamines of para-substituted propiophenones are determined at pH 4.7, the r value is positive; however, when the rates of hydrolysis are determined at pH 10.4, the r value is negative.
a. What is the rate-determining step of the hydrolysis reaction when it is carried out in a basic solution?
b. What is the rate-determining step of the hydrolysis reaction when it is carried out in an acidic solution?

σ or substituent constant : electron-withdrawing substituents have positive substituent constants and electron- donating substituents have negative substituent constants.
When log(K0 ) vs σ is plotted the slope is called rho value (ρ )
ρ or reaction constant : negative ρ value indicates that molecules with electron donation groups reacts faster than compounds with electron withdrowing groups.
Again positive ρ value indicates the eletron-withdrowing groups are reacted faster than compounds with electron donating groups.
The ρ value is negative in basic solution indicates that electron donating group increases the rate. It tells that the slowest step will be carbocation formation step ,because more negative charge on the carbon means more electron donation of the substituent and easy to protonate.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images









