Given the coordinate matrix of x relative to a (nonstandard) basis B for R", find the coordinate matrix of x relative to the standard basis. B = ((4, -1), (0, 1)), [x]s= [x] = 11
Given the coordinate matrix of x relative to a (nonstandard) basis B for R", find the coordinate matrix of x relative to the standard basis. B = ((4, -1), (0, 1)), [x]s= [x] = 11
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305658004
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Ron Larson
Chapter7: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Section7.CM: Cumulative Review
Problem 31CM
Related questions
Question
![**Topic: Coordinate Matrices and Basis**
**Problem Statement:**
Given the coordinate matrix of \( \mathbf{x} \) relative to a (nonstandard) basis \( B \) for \( \mathbb{R}^n \), find the coordinate matrix of \( \mathbf{x} \) relative to the standard basis.
**Details:**
- **Basis \( B \) for \( \mathbb{R}^n \):**
\[
B = \{ (4, -1), (0, 1) \}
\]
- **Coordinate Matrix of \( \mathbf{x} \) relative to \( B \), denoted by \( [\mathbf{x}]_B \):**
\[
[\mathbf{x}]_B = \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ 5 \end{bmatrix}
\]
- **Objective:**
Find the coordinate matrix of \( \mathbf{x} \) relative to the standard basis, denoted by \( [\mathbf{x}]_S \).
**Explanation of Diagram:**
The image illustrates the transition from the coordinate representation of a vector with respect to a nonstandard basis \( B \) to its representation with respect to the standard basis \( S \). The matrices are stacked vertically with an arrow indicating the transformation process.
**Steps to Solve:**
1. **Identify the transformation matrix:**
- To switch from basis \( B \) to the standard basis, use the transformation matrix derived from the vectors of \( B \):
\[
P_B = \begin{bmatrix} 4 & 0 \\ -1 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
\]
2. **Calculate \( [\mathbf{x}]_S \):**
- Multiply the transformation matrix \( P_B \) by the given coordinate matrix \( [\mathbf{x}]_B \).
\[
[\mathbf{x}]_S = P_B \cdot [\mathbf{x}]_B = \begin{bmatrix} 4 & 0 \\ -1 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ 5 \end{bmatrix}
\]
3. **Perform the matrix multiplication:**
- Calculate each component of the resulting vector:
\[
[\mathbf{x}]_S = \begin{bmatrix} (](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Ff821f9aa-4788-41c9-90a4-53f493bbfa90%2F095a3d3b-da2b-456c-ad6d-1d42e2a2de07%2Fv3j3nmvy_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Topic: Coordinate Matrices and Basis**
**Problem Statement:**
Given the coordinate matrix of \( \mathbf{x} \) relative to a (nonstandard) basis \( B \) for \( \mathbb{R}^n \), find the coordinate matrix of \( \mathbf{x} \) relative to the standard basis.
**Details:**
- **Basis \( B \) for \( \mathbb{R}^n \):**
\[
B = \{ (4, -1), (0, 1) \}
\]
- **Coordinate Matrix of \( \mathbf{x} \) relative to \( B \), denoted by \( [\mathbf{x}]_B \):**
\[
[\mathbf{x}]_B = \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ 5 \end{bmatrix}
\]
- **Objective:**
Find the coordinate matrix of \( \mathbf{x} \) relative to the standard basis, denoted by \( [\mathbf{x}]_S \).
**Explanation of Diagram:**
The image illustrates the transition from the coordinate representation of a vector with respect to a nonstandard basis \( B \) to its representation with respect to the standard basis \( S \). The matrices are stacked vertically with an arrow indicating the transformation process.
**Steps to Solve:**
1. **Identify the transformation matrix:**
- To switch from basis \( B \) to the standard basis, use the transformation matrix derived from the vectors of \( B \):
\[
P_B = \begin{bmatrix} 4 & 0 \\ -1 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
\]
2. **Calculate \( [\mathbf{x}]_S \):**
- Multiply the transformation matrix \( P_B \) by the given coordinate matrix \( [\mathbf{x}]_B \).
\[
[\mathbf{x}]_S = P_B \cdot [\mathbf{x}]_B = \begin{bmatrix} 4 & 0 \\ -1 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ 5 \end{bmatrix}
\]
3. **Perform the matrix multiplication:**
- Calculate each component of the resulting vector:
\[
[\mathbf{x}]_S = \begin{bmatrix} (
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given that,
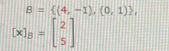
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning