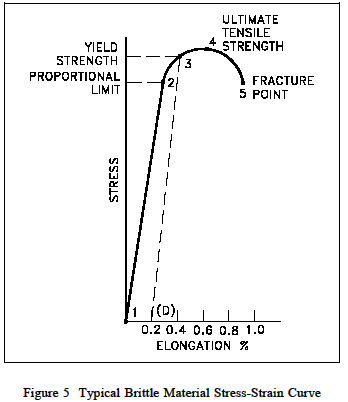
Give the information requested below. a) On the stress-strain graph below determine the yield strength. Be sure to sketch precisely how you do this. b) Determine the value for the modulus of elasticity for this material. c) Determine the value for the modulus of resilience for this material.
Give the information requested below.
a) On the stress-strain graph below determine the yield strength. Be sure to sketch precisely how you do this.
b) Determine the value for the modulus of elasticity for this material.
c) Determine the value for the modulus of resilience for this material.
d) Estimate the toughness of this material.
e) What is the ductility (%EL) of this material?

Yield strength:- The yield strength is defined as the point at which the material starts to deform plastically.
So observe the graph where the material gets deformed and mark that point as yield strength.
In case of some Brittle materials
To find yield strength, the predetermined amount of permanent strain is set along the strain axis of the graph, to the right of the origin (zero). A straight line is drawn through Point (permanent strain) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stress-strain curve.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









