Gaseous hydrogen iodide is placed in a closed container at 425° C, where it partially decomposes to hydrogen and iodine: 2HI(g) = H₂(g) + I₂(g) At equilibrium it is found that [HI] = 3.59×10-3 M . [H₂] = 4.87×104 M, and [I2] = 4.87x10-4 M. ▼ Part A What is the value of Ke at this temperature? Express the equilibrium constant to three significant digits. K₁= 54.3 Submit 195| ΑΣΦ Provide Feedback Previous Answers Request Answer Review | Constants I Periodic 1 ? X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining The equilibrium constant, Ke, of a reaction is the ratio of the molar concentrations of the products over the reactants. The answer you provided corresponds to the ratio of the reactants over the products. Next
Gaseous hydrogen iodide is placed in a closed container at 425° C, where it partially decomposes to hydrogen and iodine: 2HI(g) = H₂(g) + I₂(g) At equilibrium it is found that [HI] = 3.59×10-3 M . [H₂] = 4.87×104 M, and [I2] = 4.87x10-4 M. ▼ Part A What is the value of Ke at this temperature? Express the equilibrium constant to three significant digits. K₁= 54.3 Submit 195| ΑΣΦ Provide Feedback Previous Answers Request Answer Review | Constants I Periodic 1 ? X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining The equilibrium constant, Ke, of a reaction is the ratio of the molar concentrations of the products over the reactants. The answer you provided corresponds to the ratio of the reactants over the products. Next
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
I’m stuck. I keep getting it wrong.
![**Equilibrium Constant Calculation: Decomposition of Hydrogen Iodide**
In this exercise, gaseous hydrogen iodide (HI) is placed in a closed container at 425°C, where it partially decomposes into hydrogen (H₂) and iodine (I₂). The chemical equilibrium reaction is represented as:
\[ 2\text{HI}(g) \rightleftharpoons \text{H}_2(g) + \text{I}_2(g) \]
At equilibrium, the following concentrations are observed:
- \([\text{HI}] = 3.59 \times 10^{-3}\, M\)
- \([\text{H}_2] = 4.87 \times 10^{-4}\, M\)
- \([\text{I}_2] = 4.87 \times 10^{-4}\, M\)
**Part A:**
**Question:** What is the value of \( K_c \) at this temperature?
**Instruction:** Express the equilibrium constant (\( K_c \)) to three significant digits.
**Input Box:**
\[ K_c = \]
**Submitted Answer:**
\[ 54.3 \]
**Feedback:**
- **Incorrect; Try Again. 5 attempts remaining.**
- **Explanation:** The equilibrium constant, \( K_c \), of a reaction is the ratio of the molar concentrations of the products over the reactants, raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients. The answer provided corresponds to the ratio of the reactants over the products, which is incorrect.
**Next Steps:** Review your calculations and attempt submission again.
**Additional Resources:**
- [Constants]
- [Periodic Table]
For more detailed guidance, refer to the related instructional materials on calculating equilibrium constants.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fb0be78df-234d-4653-8235-8227b9098990%2Fa7b12d2c-df73-4380-a09e-8e78afc1230c%2Fad4ifz_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Equilibrium Constant Calculation: Decomposition of Hydrogen Iodide**
In this exercise, gaseous hydrogen iodide (HI) is placed in a closed container at 425°C, where it partially decomposes into hydrogen (H₂) and iodine (I₂). The chemical equilibrium reaction is represented as:
\[ 2\text{HI}(g) \rightleftharpoons \text{H}_2(g) + \text{I}_2(g) \]
At equilibrium, the following concentrations are observed:
- \([\text{HI}] = 3.59 \times 10^{-3}\, M\)
- \([\text{H}_2] = 4.87 \times 10^{-4}\, M\)
- \([\text{I}_2] = 4.87 \times 10^{-4}\, M\)
**Part A:**
**Question:** What is the value of \( K_c \) at this temperature?
**Instruction:** Express the equilibrium constant (\( K_c \)) to three significant digits.
**Input Box:**
\[ K_c = \]
**Submitted Answer:**
\[ 54.3 \]
**Feedback:**
- **Incorrect; Try Again. 5 attempts remaining.**
- **Explanation:** The equilibrium constant, \( K_c \), of a reaction is the ratio of the molar concentrations of the products over the reactants, raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients. The answer provided corresponds to the ratio of the reactants over the products, which is incorrect.
**Next Steps:** Review your calculations and attempt submission again.
**Additional Resources:**
- [Constants]
- [Periodic Table]
For more detailed guidance, refer to the related instructional materials on calculating equilibrium constants.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given data :
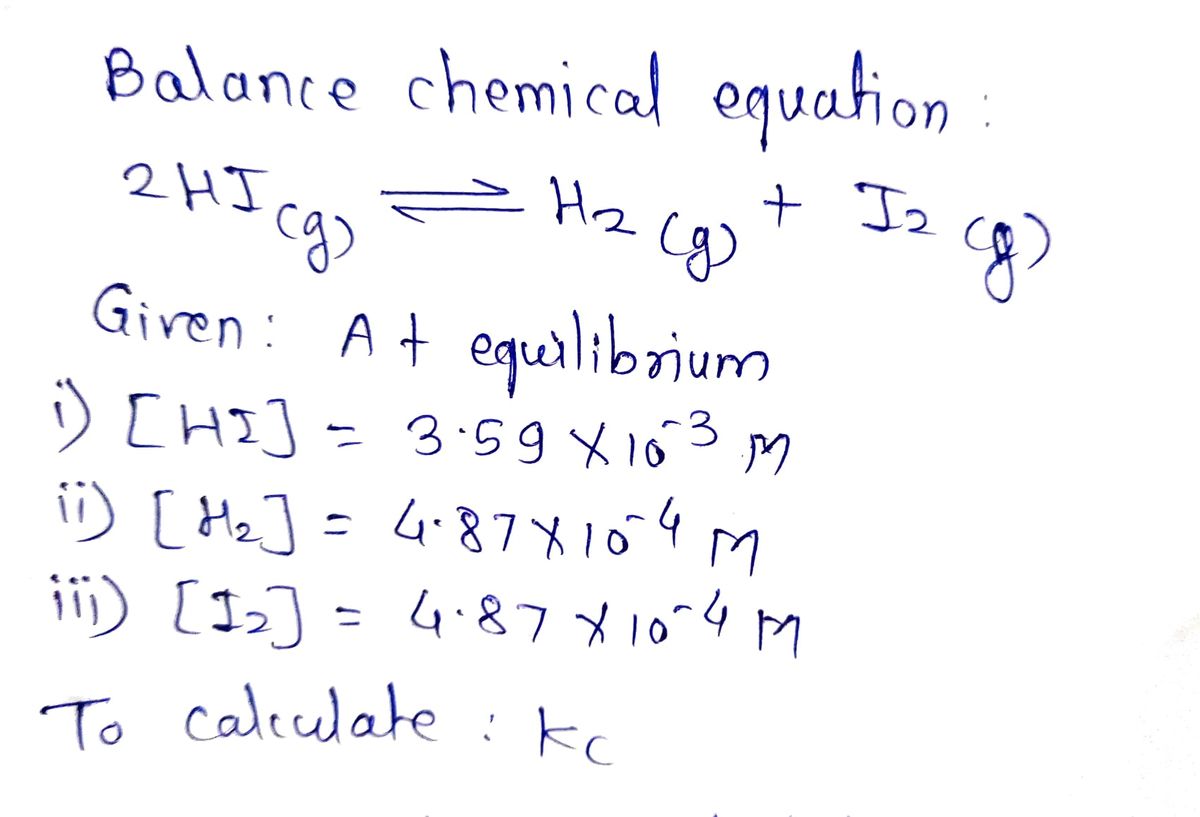
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY