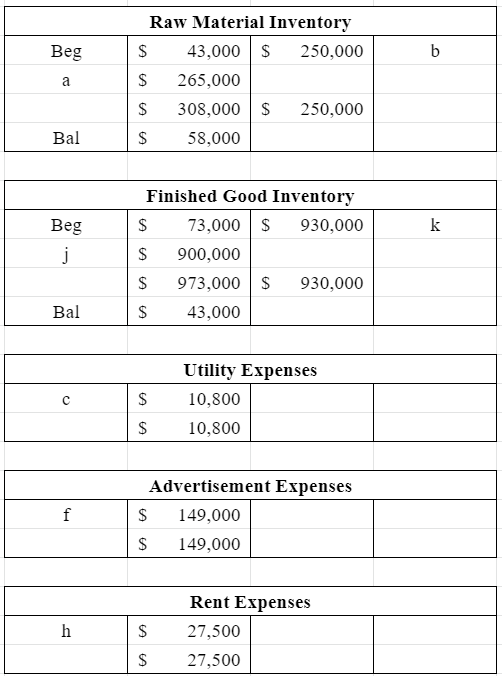
Froya Fabrikker A/S of Bergen, Norway, is a small company that manufactures specialty heavy equipment for use in North Sea oil fields. The company uses a job-order costing system that applies manufacturing overhead cost to jobs on the basis of direct labor-hours. Its predetermined overhead rate was based on a cost formula that estimated $351,000 of manufacturing overhead for an estimated allocation base of 900 direct labor-hours. The following transactions took place during the year: Raw materials purchased on account, $265,000. Raw materials used in production (all direct materials), $250,000. Utility bills incurred on account, $72,000 (85% related to factory operations, and the remainder related to selling and administrative activities). Accrued salary and wage costs: Direct labor (980 hours) $ 295,000 Indirect labor $ 103,000 Selling and administrative salaries $ 175,000 Maintenance costs incurred on account in the factory, $67,000 Advertising costs incurred on account, $149,000. Depreciation was recorded for the year, $85,000 (70% related to factory equipment, and the remainder related to selling and administrative equipment). Rental cost incurred on account, $110,000 (75% related to factory facilities, and the remainder related to selling and administrative facilities). Manufacturing overhead cost was applied to jobs, $ ? . Cost of goods manufactured for the year, $900,000. Sales for the year (all on account) totaled $1,850,000. These goods cost $930,000 according to their job cost sheets. The balances in the inventory accounts at the beginning of the year were: Raw Materials $ 43,000 Work in Process $ 34,000 Finished Goods $ 73,000 1. Prepare journal entries to record the preceding transactions. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. No Transaction General Journal Debit Credit 1 a. Raw materials 265,000 Accounts payable 265,000 2 b. Work in process 250,000 Raw materials 250,000 3 c. Manufacturing overhead 61,200 Utilities expense 10,800 Accounts payable 72,000 4 d. Work in process 295,000 Manufacturing overhead 103,000 Salaries expense 175,000 Salaries and wages payable 573,000 5 e. Manufacturing overhead 67,000 Accounts payable 67,000 6 f. Advertising expense 149,000 Accounts payable 149,000 7 g. Manufacturing overhead 59,500 Depreciation expense 25,500 Accumulated depreciation 85,000 8 h. Manufacturing overhead 82,500 Rent expense 27,500 Accounts payable 110,000 9 i. Work in process 382,200 Manufacturing overhead 382,200 10 j. Finished goods 900,000 Work in process 900,000 11 k(1). Accounts receivable 1,850,000 Sales 1,850,000 12 k(2). Cost of goods sold 930,000 Finished goods 930,000 2. Post your entries to T-accounts. (Don’t forget to enter the beginning inventory balances above.) The format for this is in the image attached and please also include the corresponding letters .
Variance Analysis
In layman's terms, variance analysis is an analysis of a difference between planned and actual behavior. Variance analysis is mainly used by the companies to maintain a control over a business. After analyzing differences, companies find the reasons for the variance so that the necessary steps should be taken to correct that variance.
Standard Costing
The standard cost system is the expected cost per unit product manufactured and it helps in estimating the deviations and controlling them as well as fixing the selling price of the product. For example, it helps to plan the cost for the coming year on the various expenses.
Froya Fabrikker A/S of Bergen, Norway, is a small company that manufactures specialty heavy equipment for use in North Sea oil fields. The company uses a job-order costing system that applies
- Raw materials purchased on account, $265,000.
- Raw materials used in production (all direct materials), $250,000.
- Utility bills incurred on account, $72,000 (85% related to factory operations, and the remainder related to selling and administrative activities).
- Accrued salary and wage costs:
| Direct labor (980 hours) | $ | 295,000 |
| Indirect labor | $ | 103,000 |
| Selling and administrative salaries | $ |
175,000 |
- Maintenance costs incurred on account in the factory, $67,000
- Advertising costs incurred on account, $149,000.
Depreciation was recorded for the year, $85,000 (70% related to factory equipment, and the remainder related to selling and administrative equipment).- Rental cost incurred on account, $110,000 (75% related to factory facilities, and the remainder related to selling and administrative facilities).
- Manufacturing overhead cost was applied to jobs, $ ? .
- Cost of goods manufactured for the year, $900,000.
- Sales for the year (all on account) totaled $1,850,000. These goods cost $930,000 according to their
job cost sheets.
The balances in the inventory accounts at the beginning of the year were:
| Raw Materials | $ | 43,000 |
| Work in Process | $ | 34,000 |
| Finished Goods | $ | 73,000 |
1. Prepare journal entries to record the preceding transactions. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No
| No | Transaction | General Journal | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a. | Raw materials | 265,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 265,000 | |||
| 2 | b. | Work in process | 250,000 | |
| Raw materials | 250,000 | |||
| 3 | c. | Manufacturing overhead | 61,200 | |
| Utilities expense | 10,800 | |||
| Accounts payable | 72,000 | |||
| 4 | d. | Work in process | 295,000 | |
| Manufacturing overhead | 103,000 | |||
| Salaries expense | 175,000 | |||
| Salaries and wages payable | 573,000 | |||
| 5 | e. | Manufacturing overhead | 67,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 67,000 | |||
| 6 | f. | Advertising expense | 149,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 149,000 | |||
| 7 | g. | Manufacturing overhead | 59,500 | |
| Depreciation expense | 25,500 | |||
| 85,000 | ||||
| 8 | h. | Manufacturing overhead | 82,500 | |
| Rent expense | 27,500 | |||
| Accounts payable | 110,000 | |||
| 9 | i. | Work in process | 382,200 | |
| Manufacturing overhead | 382,200 | |||
| 10 | j. | Finished goods | 900,000 | |
| Work in process | 900,000 | |||
| 11 | k(1). | 1,850,000 | ||
| Sales | 1,850,000 | |||
| 12 | k(2). | Cost of goods sold | 930,000 | |
| Finished goods | 930,000 |
2.


Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images









