Four straight, current-carrying wires are perpendicular to the sheet of paper you’re currently staring at which we take to be in the xy-plane. Current 1 has magnitude 5 A, points out of the paper, and passes through point (−2 cm,0 cm). Current 2 has magnitude 7 A, points into the paper, and passes through the point (2 cm,0 cm). Current 3 has magnitude 17 A, points into the paper, and passes through the point (−2 cm,2 √ 3 cm). Current 4 has magnitude 17 A, points into the paper, and passes through the point (2 cm,2 √ 3 cm). Compute the values of Bx , By , and |B|, the x- and y-components of the magnetic field at the point (0 cm,2 √ 3 cm).
Four straight, current-carrying wires are perpendicular to the sheet of paper you’re currently staring at which we take to be in the xy-plane. Current 1 has magnitude 5 A, points out of the paper, and passes through point (−2 cm,0 cm). Current 2 has magnitude 7 A, points into the paper, and passes through the point (2 cm,0 cm). Current 3 has magnitude 17 A, points into the paper, and passes through the point (−2 cm,2 √ 3 cm). Current 4 has magnitude 17 A, points into the paper, and passes through the point (2 cm,2 √ 3 cm). Compute the values of Bx , By , and |B|, the x- and y-components of the magnetic field at the point (0 cm,2 √ 3 cm).
Scenario: When current passes through a conducting wire, magnetic field is created around it. Magnetic filed intensity varies based on value of current, the conductor carries. Direction of magnetic field also changes depending on direction of current
The given data are,
The drections and components of the magnetic field at P are shown in the figure.
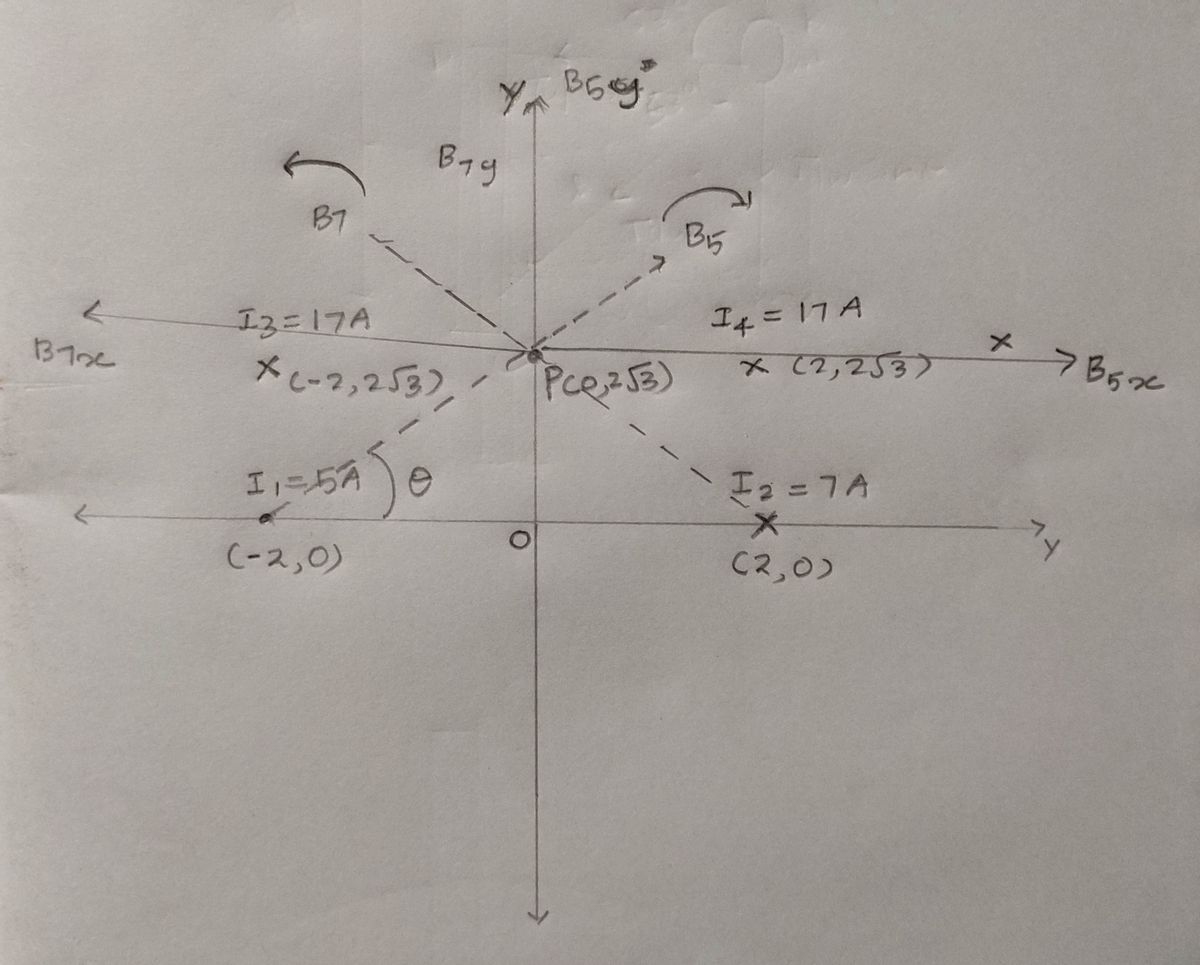
From the figure,
From the triangle
so,
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 1 images









