For this problem, one mole of a diatomic ideal gas is taken around a reversible cycle by starting at pressure P, volume V, and temperature T, then in an isochoric process 1 increasing pressure to 6P, then in an isobaric process 2 increasing its volume to 21V, then another isochoric process 3 back to a pressure P, and finally in an isobaric process 4 back to P, V, T. Find the temperature of this gas at the end of process 1, 2, and 3 in terms of the original temperature T. Find the internal energy change in process 1 and in process 2 in terms of P and V. Find the heat transfer in process 1 and in process 2 in terms of P and V.
For this problem, one mole of a diatomic ideal gas is taken around a reversible cycle by starting at pressure P, volume V, and temperature T, then in an isochoric process 1 increasing pressure to 6P, then in an isobaric process 2 increasing its volume to 21V, then another isochoric process 3 back to a pressure P, and finally in an isobaric process 4 back to P, V, T. Find the temperature of this gas at the end of process 1, 2, and 3 in terms of the original temperature T. Find the internal energy change in process 1 and in process 2 in terms of P and V. Find the heat transfer in process 1 and in process 2 in terms of P and V.
Related questions
Question
Problem #2: For this problem, one mole of a diatomic ideal gas is taken around a reversible cycle by starting at pressure P, volume V, and temperature T, then in an isochoric process 1 increasing pressure to 6P, then in an isobaric process 2 increasing its volume to 21V, then another isochoric process 3 back to a pressure P, and finally in an isobaric process 4 back to P, V, T.
- Find the temperature of this gas at the end of process 1, 2, and 3 in terms of the original temperature T.
- Find the internal energy change in process 1 and in process 2 in terms of P and V.
- Find the heat transfer in process 1 and in process 2 in terms of P and V.
Expert Solution
Step 1
(1) Temperature at the end of each process
Process 1 is isochoric.
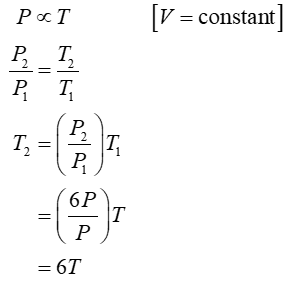
Step 2
Process 2 is isobaric
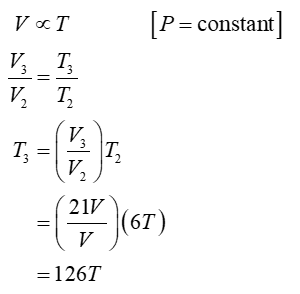
Step 3
Process 3 is isochoric
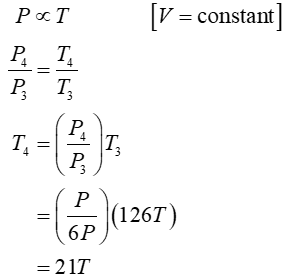
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 7 images
