Find the Riemann sum for f(x) = x² + 3x over the interval [0, 8] (see figure), where Xo = 0, X₁ = 1, X₂ = 2, X3 = 4, and X4 8, = and where C₁ = 1, C₂ = 2, C3 = 4, and c4 = 8. y 100 80 60 40 20 - 20 2 4 6 8 10 X
Find the Riemann sum for f(x) = x² + 3x over the interval [0, 8] (see figure), where Xo = 0, X₁ = 1, X₂ = 2, X3 = 4, and X4 8, = and where C₁ = 1, C₂ = 2, C3 = 4, and c4 = 8. y 100 80 60 40 20 - 20 2 4 6 8 10 X
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
100%
![**Problem Statement:**
Find the Riemann sum for \( f(x) = x^2 + 3x \) over the interval \([0, 8]\) (see figure), where
\[ x_0 = 0, \, x_1 = 1, \, x_2 = 2, \, x_3 = 4, \, \text{and} \, x_4 = 8, \]
and where
\[ c_1 = 1, \, c_2 = 2, \, c_3 = 4, \, \text{and} \, c_4 = 8. \]
**Graph Explanation:**
The graph illustrates the function \( f(x) = x^2 + 3x \). The curve is plotted over the interval \([0, 8]\). It is a parabola opening upwards, increasing more steeply as \( x \) increases. The shaded region under the curve from \( x=0 \) to \( x=8 \) represents the area being approximated by the Riemann sum. The graph effectively shows how the function values and the interval endpoints contribute to calculating the Riemann sum approximation for the integral of \( f(x) \).](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F9ba58da1-aa6c-4b34-ac65-53856b97f0bf%2Fb0835ee8-f14b-404f-9551-4a5348cb7d7d%2F6dwpmx_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
Find the Riemann sum for \( f(x) = x^2 + 3x \) over the interval \([0, 8]\) (see figure), where
\[ x_0 = 0, \, x_1 = 1, \, x_2 = 2, \, x_3 = 4, \, \text{and} \, x_4 = 8, \]
and where
\[ c_1 = 1, \, c_2 = 2, \, c_3 = 4, \, \text{and} \, c_4 = 8. \]
**Graph Explanation:**
The graph illustrates the function \( f(x) = x^2 + 3x \). The curve is plotted over the interval \([0, 8]\). It is a parabola opening upwards, increasing more steeply as \( x \) increases. The shaded region under the curve from \( x=0 \) to \( x=8 \) represents the area being approximated by the Riemann sum. The graph effectively shows how the function values and the interval endpoints contribute to calculating the Riemann sum approximation for the integral of \( f(x) \).
Expert Solution
Step 1: Given
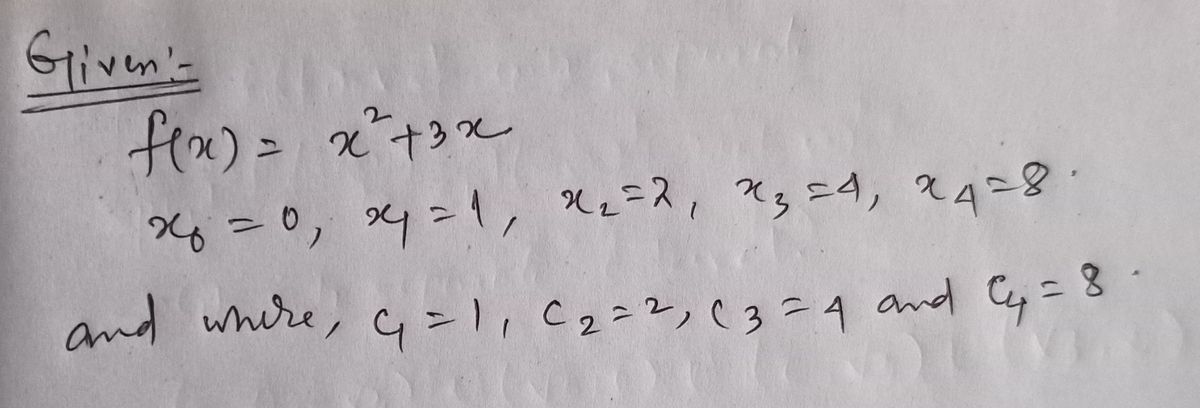
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning