UniQ is a company that produces speaker HF drivers and woofers in the UK. Their largest consumer is KEF, a UK loudspeaker manufacturing company. The manager of KEF has asked the research department to find out how sensitive KEF’s
U(x,y) = x^1/2 y^1/2
The price for one unit of woofer is equal to £1. It is estimated that KEF’s budget is £10,000. Find the price-consumption curve for HF drivers and the corresponding demand curve.
A price consumption curve for good x can be defined as a locus of combinations of good x that would be demanded by the given consumer at different levels of prices of that good.
Figure (1) below depicts the required price-consumption curve for good x
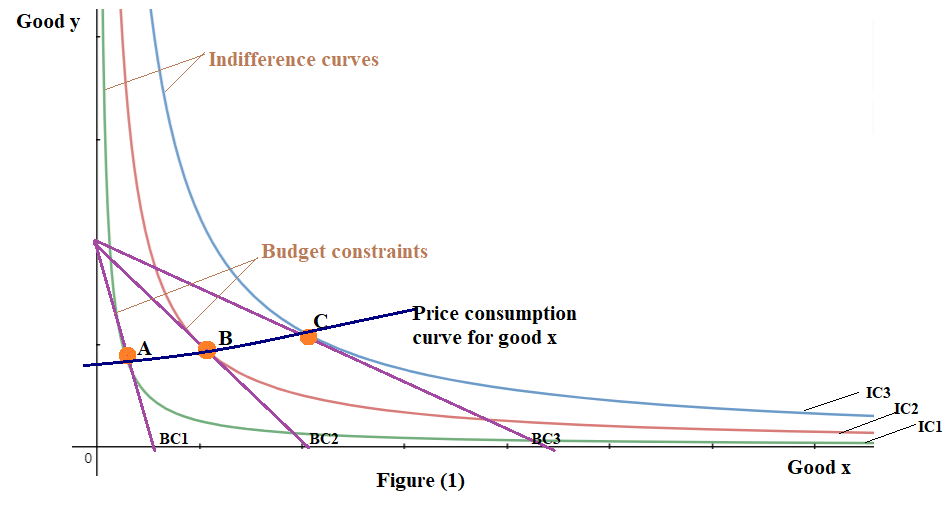
In figure (1)
The BC1 is the initial budget constraint of the consumer.
The indifference curves IC1, IC2, and IC3 depict the indifference map of the consumer.
When the price of good x falls, then BC1 rotates along the X-axis to BC2. And when the price falls further than, it rotates to BC3.
The combinations of good x demanded by the consumer are given by the points A, B, and C at which the indifference curves IC1, IC2, and IC3 intersect the budget constraints BC1, BC2, and BC3 respectively.
Thus, as per the meaning of the price consumption curve, the curve joining A,B and C would result in the required price consumption of the good x.
The budget constraint of the given consumer can be written as follows,
xPx + yPx = M (1)
Here,
x and y depict the quantity of goods x and y respectively
Px and Py depict the price of goods x and y respectively
M depicts the income/budget.
Plug Py = 1 and m = 10,000 in (1) to get the required budget constraint,
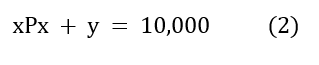
The slope of the budget constraint is given as Px/Py.
This implies that,
Slope of budget constraint = Px/1 = Px
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 7 images









