Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
I need help solving this chain rule problem. I tried to solve it, but I'm a little confused on how to continue
![The image contains a step-by-step differentiation process using the chain rule and quotient rule. Here's a transcription and explanation:
1. **Starting Expression:**
\[
y = \left( \frac{x}{x+3} \right)^{1/2} = u^{1/2}
\]
2. **Substitution:**
\[
u = \frac{x}{x+3}
\]
3. **Functions Definition:**
\[
f(u) = u^{1/2} \quad g(x) = \frac{x}{x+3}
\]
4. **Expression for y:**
\[
y = \left( \frac{x}{x+3} \right)^{1/2}
\]
5. **Derivative Start:**
\[
y' = \frac{d}{dx} \left( \left( \frac{x}{x+3} \right)^{1/2} \right)
\]
6. **Chain Rule Application:**
\[
y' = \frac{1}{2} \left( u \right)^{-1/2} \cdot \frac{d}{dx} \left( \frac{x}{x+3} \right)
\]
- Use the quotient rule for \(\frac{x}{x+3}\).
7. **Quotient Rule Application:**
\[
y' = \frac{1}{2} \cdot u^{-1/2} \cdot \frac{(x+3)(1) - (x)(1)}{(x+3)^2}
\]
8. **Simplified Derivative:**
\[
y' = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \left( \frac{x}{x+3} \right)^{-1/2} \cdot \frac{3}{(x+3)^2}
\]
9. **Final Simplified Form:**
\[
y' = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{\frac{x}{x+3}}} \cdot \frac{3}{(x+3)^2}
\]
\[
y' = \frac{3}{2} \cdot \frac{1}{\](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F3eb03a80-7cae-4d33-b228-e2e0361c370e%2F4074b4b9-9c4f-4291-8ec6-5c703753ef70%2Fg3agoe7_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:The image contains a step-by-step differentiation process using the chain rule and quotient rule. Here's a transcription and explanation:
1. **Starting Expression:**
\[
y = \left( \frac{x}{x+3} \right)^{1/2} = u^{1/2}
\]
2. **Substitution:**
\[
u = \frac{x}{x+3}
\]
3. **Functions Definition:**
\[
f(u) = u^{1/2} \quad g(x) = \frac{x}{x+3}
\]
4. **Expression for y:**
\[
y = \left( \frac{x}{x+3} \right)^{1/2}
\]
5. **Derivative Start:**
\[
y' = \frac{d}{dx} \left( \left( \frac{x}{x+3} \right)^{1/2} \right)
\]
6. **Chain Rule Application:**
\[
y' = \frac{1}{2} \left( u \right)^{-1/2} \cdot \frac{d}{dx} \left( \frac{x}{x+3} \right)
\]
- Use the quotient rule for \(\frac{x}{x+3}\).
7. **Quotient Rule Application:**
\[
y' = \frac{1}{2} \cdot u^{-1/2} \cdot \frac{(x+3)(1) - (x)(1)}{(x+3)^2}
\]
8. **Simplified Derivative:**
\[
y' = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \left( \frac{x}{x+3} \right)^{-1/2} \cdot \frac{3}{(x+3)^2}
\]
9. **Final Simplified Form:**
\[
y' = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{\frac{x}{x+3}}} \cdot \frac{3}{(x+3)^2}
\]
\[
y' = \frac{3}{2} \cdot \frac{1}{\
![**Problem Statement:**
Find the derivative of the function.
\[ y = \sqrt{\frac{x}{x + 3}} \]
**Explanation:**
In this problem, we are asked to find the derivative of the function \( y \), which is defined as the square root of the fraction \(\frac{x}{x+3}\).
To solve this, we apply the chain rule and quotient rule for derivatives.
1. **Chain Rule:**
- If \( y = \sqrt{u} \), then \( \frac{dy}{du} = \frac{1}{2\sqrt{u}} \).
2. **Quotient Rule**:
- For a function \( u = \frac{f(x)}{g(x)} \), the derivative \( \frac{du}{dx} = \frac{f'(x)g(x) - f(x)g'(x)}{[g(x)]^2} \).
Using these rules will help find the derivative for more complex functions like the given one.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F3eb03a80-7cae-4d33-b228-e2e0361c370e%2F4074b4b9-9c4f-4291-8ec6-5c703753ef70%2Fgscsen_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
Find the derivative of the function.
\[ y = \sqrt{\frac{x}{x + 3}} \]
**Explanation:**
In this problem, we are asked to find the derivative of the function \( y \), which is defined as the square root of the fraction \(\frac{x}{x+3}\).
To solve this, we apply the chain rule and quotient rule for derivatives.
1. **Chain Rule:**
- If \( y = \sqrt{u} \), then \( \frac{dy}{du} = \frac{1}{2\sqrt{u}} \).
2. **Quotient Rule**:
- For a function \( u = \frac{f(x)}{g(x)} \), the derivative \( \frac{du}{dx} = \frac{f'(x)g(x) - f(x)g'(x)}{[g(x)]^2} \).
Using these rules will help find the derivative for more complex functions like the given one.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Derivative property used :
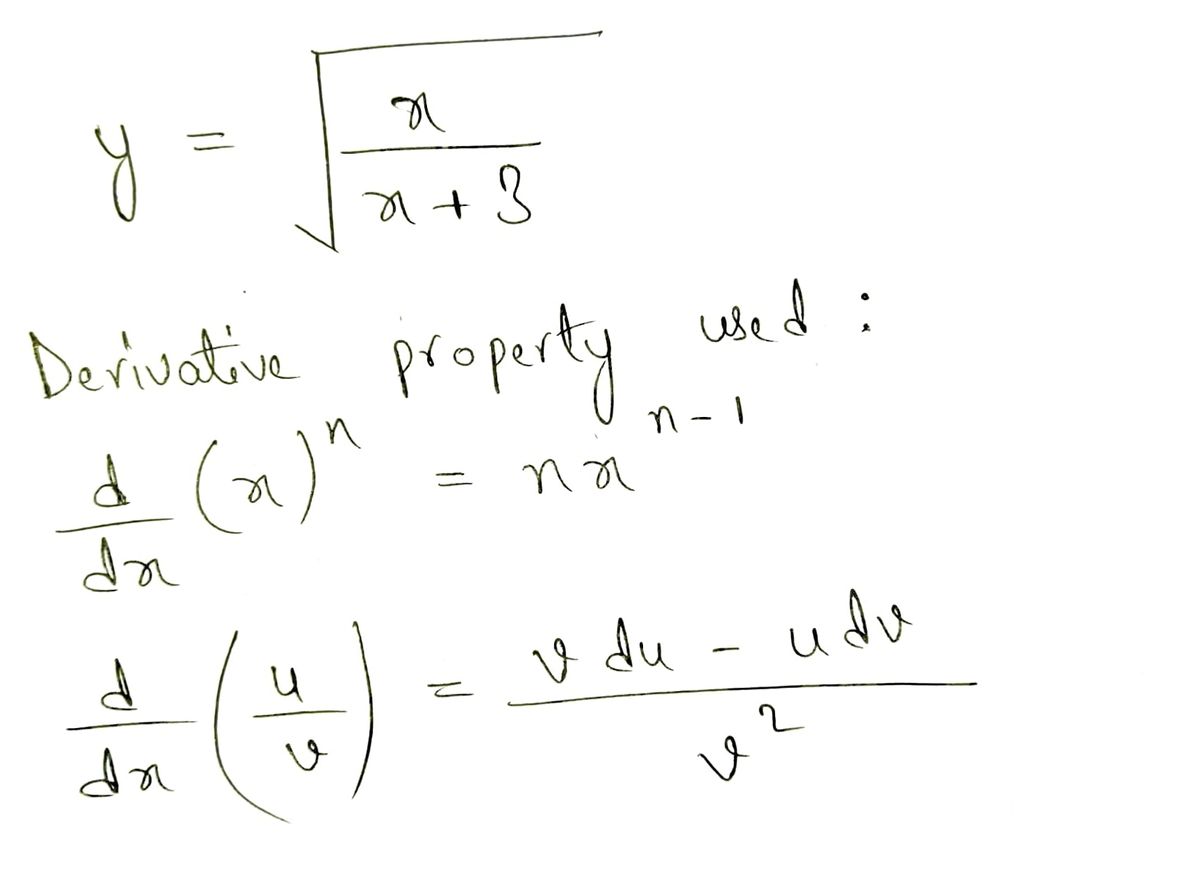
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning