Find the average pressure on the vertical surface of the quadrant and calculate the theoretical magnitude of the resultant force FR for each measurement. For this step, you only need to take. into account the submerged depth of the surface. 1. Table 1. Create a table and include the depth of the water (mm) from your laboratory measurements. Add columns with the following date: depth of the water converted to meters, submerged area (in square meters), theoretical pressure at the bottom of the surface (in Pascal), average pressure on the vertical pressure (in Pascal), and theoretical hydrostatic force on the surface (in Newton). In total this table should have 6 columns.
Find the average pressure on the vertical surface of the quadrant and calculate the theoretical magnitude of the resultant force FR for each measurement. For this step, you only need to take. into account the submerged depth of the surface. 1. Table 1. Create a table and include the depth of the water (mm) from your laboratory measurements. Add columns with the following date: depth of the water converted to meters, submerged area (in square meters), theoretical pressure at the bottom of the surface (in Pascal), average pressure on the vertical pressure (in Pascal), and theoretical hydrostatic force on the surface (in Newton). In total this table should have 6 columns.
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Concept explainers
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:285mm
EDIBON 100mm-
Figure 1. Equipment for Fluid Statics Experiment.
Distance from rotating point to weight tray = 285 mm
Inner radius = 100 mm
Outer radius = 200 mm
Width of surface = 70 mm
*******
wwwwww
200mm
ACSINT PRESSURE
COM
FMEUO
MUMS
70mm

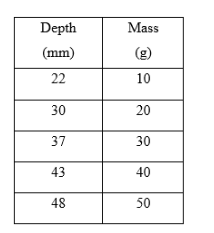
Transcribed Image Text:Data Sheet
Water Temperature = 20 °C
Depth
(mm)
22
30
37
43
48
Mass
(g)
10
20
30
40
50
Find the average pressure on the vertical surface of the quadrant and calculate the theoretical
magnitude of the resultant force FR for each measurement. For this step, you only need to take.
into account the submerged depth of the surface.
1. Table 1. Create a table and include the depth of the water (mm) from your laboratory
measurements. Add columns with the following date: depth of the water converted to meters,
submerged area (in square meters), theoretical pressure at the bottom of the surface (in Pascal).
average pressure on the vertical pressure (in Pascal), and theoretical hydrostatic force on the
surface (in Newton). In total this table should have 6 columns.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Data given

Find:
Average Pressure on the vertical surface of the quadrant and calculate the theoretical magnitude of the resultant force for each measurement.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning