Find RT, Is, 1, 12, Ix, V1, V2, and the power absorbed by the 6 ohm resistor. RT 32 + 36V 8Ω 82

In circuit shown in question, the 6Ω resistor is in parallel with 3Ω resistor and the 8Ω resistor is in parallel with another 8Ω resistor. Both the parallel combinations are in series with the 3Ω resistor. Thus, the total resistance seen by the voltage source is given by:
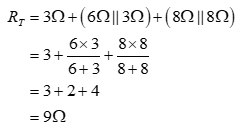
The total current supplied by the voltage source is the ratio of the voltage of voltage source and the total resistance seen by the voltage source and the same is given by:
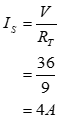
The current entering the voltage source is equal to current supplied by voltage source. The current Ix is equal to current supplied by the voltage source that is 4A.
To calculate the current through 6Ω resistor, apply current division rule across the parallel combination of 6Ω and 3Ω:
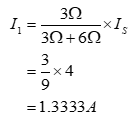
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 7 images









