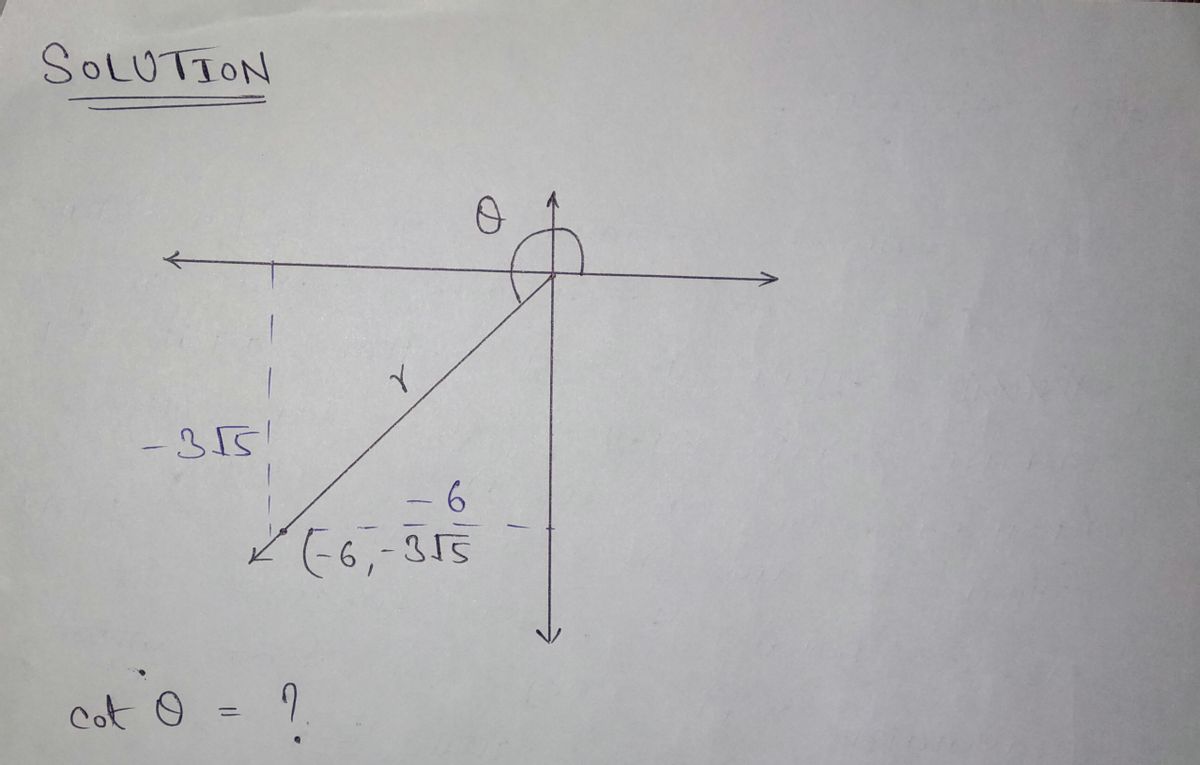
Find cot 0. [?]V] A-6, -3/5)
Trigonometry (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN:9780134217437
Author:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Chapter1: Trigonometric Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RE:
1. Give the measures of the complement and the supplement of an angle measuring 35°.
Related questions
Question
![### Finding the Cotangent of an Angle
The diagram shown is a coordinate system where an angle \(\theta\) is formed with the positive x-axis. A line extends from the origin to the point \((-6, -3\sqrt{5})\), labeled as \(r\).
#### Objective:
Calculate \(\cot \theta\).
#### Components:
- **Coordinates:**
- The point of interest is \((-6, -3\sqrt{5})\).
- **Angle \(\theta\):**
- Formed between the terminal side of angle \(\theta\) and the positive x-axis.
#### Calculation:
In trigonometry, the cotangent of an angle \(\theta\) is given by:
\[
\cot \theta = \frac{x}{y}
\]
where \(x\) and \(y\) are the coordinates of the point on the terminal side of \(\theta\).
For the point \((-6, -3\sqrt{5})\):
- \(x = -6\)
- \(y = -3\sqrt{5}\)
Thus:
\[
\cot \theta = \frac{-6}{-3\sqrt{5}} = \frac{6}{3\sqrt{5}} = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}}
\]
The boxed area in the image containing a square root suggests a simplification step:
\[
\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}
\]
This is the rationalized form of \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\).
#### Conclusion:
The cotangent of \(\theta\), \(\cot \theta\), simplifies to \(\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}\).](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F6f2c9438-5a89-4288-b691-8fe1dc913be9%2F58623b9e-e52b-4dcb-af6c-f9c18513bd2b%2Fqiubqx_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:### Finding the Cotangent of an Angle
The diagram shown is a coordinate system where an angle \(\theta\) is formed with the positive x-axis. A line extends from the origin to the point \((-6, -3\sqrt{5})\), labeled as \(r\).
#### Objective:
Calculate \(\cot \theta\).
#### Components:
- **Coordinates:**
- The point of interest is \((-6, -3\sqrt{5})\).
- **Angle \(\theta\):**
- Formed between the terminal side of angle \(\theta\) and the positive x-axis.
#### Calculation:
In trigonometry, the cotangent of an angle \(\theta\) is given by:
\[
\cot \theta = \frac{x}{y}
\]
where \(x\) and \(y\) are the coordinates of the point on the terminal side of \(\theta\).
For the point \((-6, -3\sqrt{5})\):
- \(x = -6\)
- \(y = -3\sqrt{5}\)
Thus:
\[
\cot \theta = \frac{-6}{-3\sqrt{5}} = \frac{6}{3\sqrt{5}} = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}}
\]
The boxed area in the image containing a square root suggests a simplification step:
\[
\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}
\]
This is the rationalized form of \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\).
#### Conclusion:
The cotangent of \(\theta\), \(\cot \theta\), simplifies to \(\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}\).
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9780134217437
Author:
Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher:
PEARSON

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9780134217437
Author:
Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher:
PEARSON

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning