Find and show work for: f(1,1) f(2,0) f(0,0)
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Topic: Joint probability distributions
Find and show work for:
f(1,1)
f(2,0)
f(0,0)
![96
Chapter 3 Random Variables and Probability Distributions
5, it will become clear that the joint probability distribution of Table 3.1 can
be represented by the formula
f(x, y)
Y
=
for x = 0, 1, 2; y = 0, 1, 2; and 0 ≤ x + y ≤ 2.
(b) The probability that (X, Y) fall in the region A is
P[(X, Y) € A] = P(X + Y ≤ 1) = ƒ(0,0) + ƒ(0, 1) + ƒ(1, 0)
3 3 9 9
28 14 28
14*
3
(31) (1) (2_2-y)
(8)
= + +
f(x, y)
0
1
2
Table 3.1: Joint Probability Distribution for Example 3.14
Column Totals
0
3
28
3
=
14
1
28
X
1
9
28
3
14
0
2
3
28
0
0
5
15
3
14 28 28
Row
Totals
15
28
1
28
1
When X and Y are continuous random variables, the joint density function
f(x, y) is a surface lying above the xy plane, and P[(X, Y) € A], where A is any
region in the xy plane, is equal to the volume of the right cylinder bounded by the
base A and the surface.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F53be2c08-b5df-4492-b805-ccec7f62b780%2F77c67ef1-9470-42e9-9ee0-5a57375f6589%2F0xt50eb_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:96
Chapter 3 Random Variables and Probability Distributions
5, it will become clear that the joint probability distribution of Table 3.1 can
be represented by the formula
f(x, y)
Y
=
for x = 0, 1, 2; y = 0, 1, 2; and 0 ≤ x + y ≤ 2.
(b) The probability that (X, Y) fall in the region A is
P[(X, Y) € A] = P(X + Y ≤ 1) = ƒ(0,0) + ƒ(0, 1) + ƒ(1, 0)
3 3 9 9
28 14 28
14*
3
(31) (1) (2_2-y)
(8)
= + +
f(x, y)
0
1
2
Table 3.1: Joint Probability Distribution for Example 3.14
Column Totals
0
3
28
3
=
14
1
28
X
1
9
28
3
14
0
2
3
28
0
0
5
15
3
14 28 28
Row
Totals
15
28
1
28
1
When X and Y are continuous random variables, the joint density function
f(x, y) is a surface lying above the xy plane, and P[(X, Y) € A], where A is any
region in the xy plane, is equal to the volume of the right cylinder bounded by the
base A and the surface.
Expert Solution
Step 1
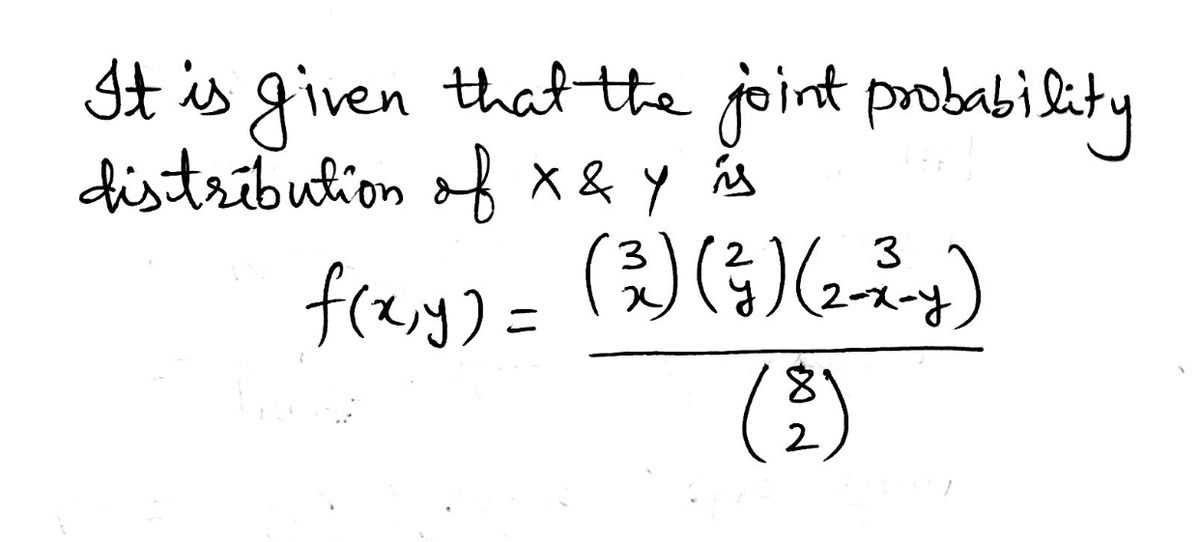
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman