Explain Five addition reactions of cyclohexene ?
Addition of Bronsted acid to an alkene produces an halo alkane.
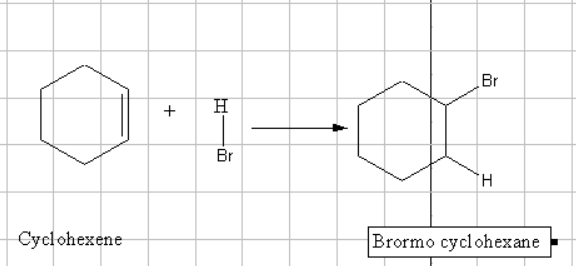
In this reaction the addition of Bronsted acid results in the addition of negative addendum to the alkene which results in the formation of a stable carbocation. Some time the shifting of function groups will also take place. This is known as Markownikoff rule. In the presence of a peroxide this eill result in the formation of a less stable carbocation which gets stabilized by rearrangement.
Addition of Lewis acid to alkene produces alkanes with two substituents.
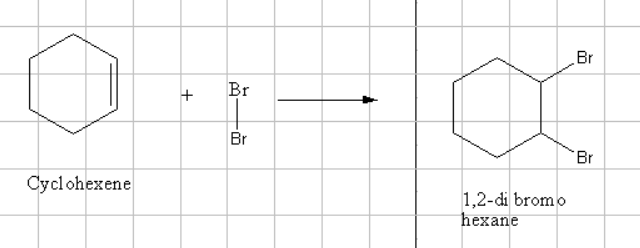
In this type of reactions there will be an heterolytic fission takes between the two halogens. The double bond present will polarize the homolytic bond present between Bromine and bromine atoms .
This will result in the formation of a carbocation in which the negative adenddum has to add such that the positive charge present should be small.
Reaction of Cyclohexene with sulfuric acid gives cyclohexyl hydrogen sulfate
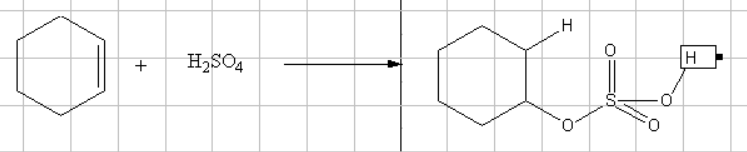
The reaction of alkene with sulfuric acid is also an electrophilic addition reaction. The acid looses its acidic proton to give the alkene a carbo cation which should be having a stable carbocation. The sulfate ion present will attack the carbocation resulting in cyclohexyl hydrogen sulfate
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images









