Exhaust gasses coming out at a rate of 'Q' m³/s from an industrial plant is passed through a packed bed of 'L' m length and 'd1' m diameter before passing it to the surroundings. The absorber bed is constructed with elements having sphericity and the diameter as 's' and 'd2' mm respectively. The bed porosity is calculated as 'p'. With the given data, evaluate the following with given data: (i) Superficial velocity of the air; [2] (ii) Reynolds number; [4] (iii) Pressure drop of air through the bed. [6] Gas Flow rate, Q = Length of bed, L Dia. of bed, d1 = Element dia., d2 Sphericity, s = Bed Porosity, p = 1.3653001 m3/s 3.2 m 1.4 m 14.2 mm %3D %3D 0.8 0.43 Note: Take viscosity and density of the exhaust gases as 1.771 x 10-5 N-s/m2 and 1.067 kg/m3.
typing only no hand written please
![Exhaust gasses coming out at a rate of 'Q' m³/s from an industrial plant is passed through a packed
bed of 'L' m length and 'd1' m diameter before passing it to the surroundings. The absorber bed is
constructed with elements having sphericity and the diameter as 's' and 'd2' mm respectively. The bed
porosity is calculated as 'p'. With the given data, evaluate the following with given data:
(i) Superficial velocity of the air; [2]
(ii) Reynolds number; [4]
(iii) Pressure drop of air through the bed. [6]
Gas Flow rate, Q =
Length of bed, L
Dia. of bed, d1 =
Element dia., d2
Sphericity, s =
Bed Porosity, p =
1.3653001 m3/s
3.2 m
1.4 m
14.2 mm
%3D
%3D
0.8
0.43
Note: Take viscosity and density of the exhaust gases as 1.771 x 10-5 N-s/m2 and 1.067 kg/m3.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F9fa9a5fe-eedd-47a8-ba69-48372ee9533b%2F6efc8dd4-e054-458c-a52d-b7cdbdf524e2%2Fgh00koa.png&w=3840&q=75)
(i) The superficial velocity of the air is to be calculated.
The superficial velocity of air is given as,
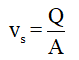 ....... (1)
....... (1)
vs = Superficial velocity
Q = Gas flow rate
A = Area of the bed
The area of the bed is given as,
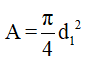 ....... (2)
....... (2)
The data given is,
Q = 1.3653001 m3/s
d1 = 1.4 m (Bed diameter)
Substitute equation (2) in equation (1) along with above data,
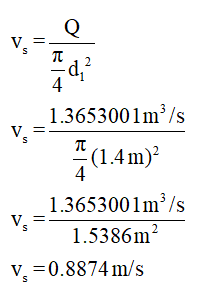
(ii) The Reynolds number for the given conditions is to be calculated.
The Reynolds number is given as,
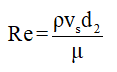 ....... (3)
....... (3)
The notations used are:-
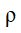 = Density of the air
= Density of the air
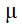 = Viscosity of the air
= Viscosity of the air
d2 = Element diameter
The data given is,
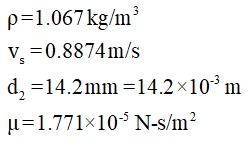
Substitute the above data in equation (3),
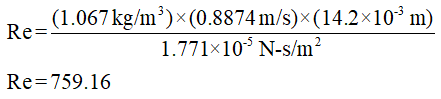
Step by step
Solved in 9 steps with 11 images









