1. A small steam superheater will be made of 0.75-in. schedule 80 stainless steel pipe which will be exposed to hot flue gas from a boiler. 50 lbm/h of saturated steam at 320 °F will enter the pipe and be heated to 380 °F. Assuming that the pipe wall temperature will vary from 375 °F at the steam inlet to 415 °F at the outlet, calculate the length of pipe required for the super heater
1. A small steam superheater will be made of 0.75-in. schedule 80 stainless steel pipe which will be exposed to hot flue gas from a boiler. 50 lbm/h of saturated steam at 320 °F will enter the pipe and be heated to 380 °F. Assuming that the pipe wall temperature will vary from 375 °F at the steam inlet to 415 °F at the outlet, calculate the length of pipe required for the super heater
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
100%
please write neat
1

Transcribed Image Text:1. A small steam superheater will be made of 0.75-in. schedule 80 stainless steel pipe which will be
exposed to hot flue gas from a boiler. 50 lbm/h of saturated steam at 320 °F will enter the pipe and
be heated to 380 °F. Assuming that the pipe wall temperature will vary from 375 °F at the steam
inlet to 415 °F at the outlet, calculate the length of pipe required for the super heater
Expert Solution
Step 1

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
everything looks great but can u plz solve for h using the appropriate nusselt equation
attached
and thens solve for L
no need to type out equations just need to make sure value is correct
thanks
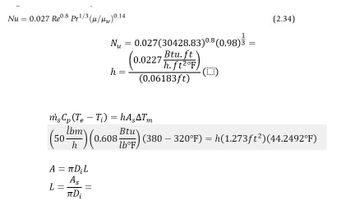
Transcribed Image Text:Nu = 0.027 Re0.8 pr¹/3 (μ/w) 0.14
A = πD;L
As
πDi
L
=
=
Nu
N₂ = 0.027 (30428.83)0.8 (0.98)3 =
Btu. ft
(0.02
(0.0227 h. ft²°F)
(0.06183ft)
msCp (Te Ti) = hA,ATm
(50m)
b) (0.608 Bor) (380 - 320°F) = h(1.273ft²)(44.2492°F)
lb°F,
=
h
(Ⓒ)
(2.34)
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY