ent on the coil. 3.A charged particle of mass m = 4 x 1012 kg and charge g=-2 µC, has a velocity v36x 10' m/s. It enters a region of space where there is a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B3D3T oriented outward with respect to the plane of this sheet as shown in the figure below. a) Use the right hand rule and show the direction of the magnetic force acting on the charge. b) Sketch the path taken by the charge within the magnetic field. c) Calculate the radius of the particle's trajectory. d) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the electric field that would allow the charge to continue moving in a straight line as it enters the magnetic field Sketch the electric field vector on the figure below. B. 7.
ent on the coil. 3.A charged particle of mass m = 4 x 1012 kg and charge g=-2 µC, has a velocity v36x 10' m/s. It enters a region of space where there is a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B3D3T oriented outward with respect to the plane of this sheet as shown in the figure below. a) Use the right hand rule and show the direction of the magnetic force acting on the charge. b) Sketch the path taken by the charge within the magnetic field. c) Calculate the radius of the particle's trajectory. d) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the electric field that would allow the charge to continue moving in a straight line as it enters the magnetic field Sketch the electric field vector on the figure below. B. 7.
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:ent on the coil.
3.A charged particle of mass m = 4 x 1012 kg and charge g=-2 µC, has a velocity
v36x 10' m/s. It enters a region of space where there is a uniform magnetic field of
magnitude B3D3T oriented outward with respect to the plane of this sheet as shown in
the figure below.
a) Use the right hand rule and show the direction of the magnetic force acting on the
charge.
b) Sketch the path taken by the charge within the magnetic field.
c) Calculate the radius of the particle's trajectory.
d) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the electric field that would allow the charge
to continue moving in a straight line as it enters the magnetic field Sketch the electric
field vector on the figure below.
B.
7.
Expert Solution
Step 1
(a) The magnetic field points out of the plane of the page and the velocity vector points upwards. For a positive charge, if the fore finger points in the direction of the velocity vector and the middle finger points in the direction of the magnetic field then the thumb points in the direction of the magnetic force.
The given charge is negative. Thus, the magnetic force points towards left.
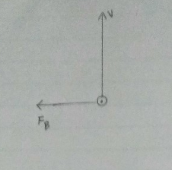
Step 2
(b) the charge is deflected towards the magnetic force. Thus, it traces a circular path in the anti-clockwise direction.
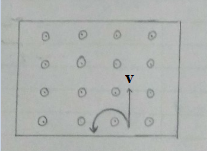
Step 3
(c) Radius of the trajectory
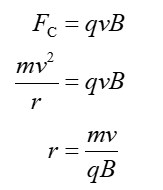
Step 4
Substitution
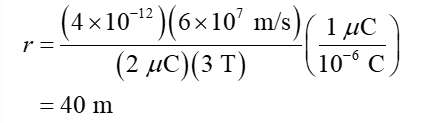
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 7 images
