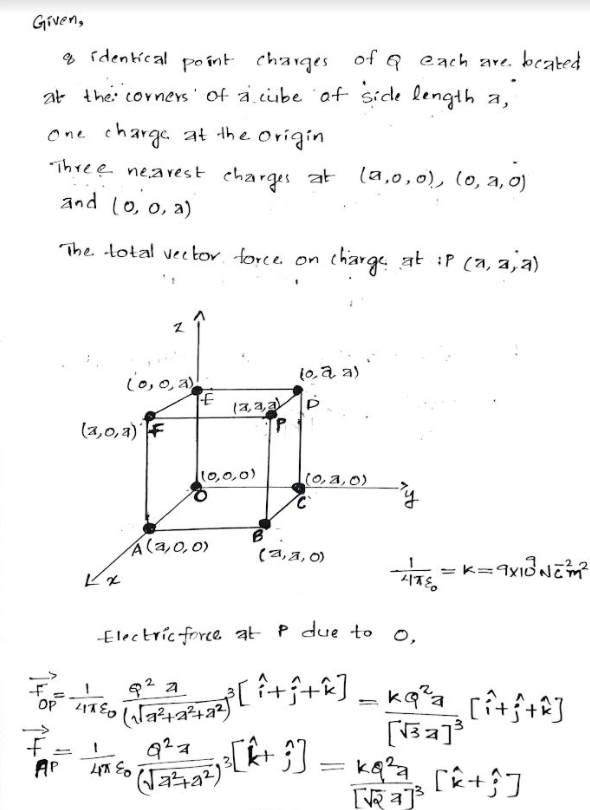
Eight identical point charges of Q C each are located at the corners of a cube of side length a, with one charge at the origin, and with the three nearest charges at (a,0,0),(0, a,0), and (0,0,a). Find an expression for the total vector force on the charge at P(a,a,a), assuming free space.
Eight identical point charges of Q C each are located at the corners of a cube of side length a, with one charge at the origin, and with the three nearest charges at (a,0,0),(0, a,0), and (0,0,a). Find an expression for the total vector force on the charge at P(a,a,a), assuming free space.
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Eight identical point charges of Q C each are located at the corners of a cube of
side length a, with one charge at the origin, and with the three nearest charges at
(a,0,0), (0, a,0), and (0,0, a). Find an expression for the total vector force on the
charge at P(a,a,a), assuming free space.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images
