Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
100%
![**Problem Statement:**
Evaluate the integral
\[
\int_{-\pi}^{\pi} \cos^2(9x) \, dx.
\]
**Explanation:**
The problem involves integrating the square of the cosine function with a multiple angle, \(9x\), over the symmetric interval \([-π, π]\).
A common technique to solve integrals of squared trigonometric functions is to use the power-reduction identity:
\[
\cos^2(\theta) = \frac{1 + \cos(2\theta)}{2}.
\]
In this case, substitute \(\theta = 9x\), so:
\[
\cos^2(9x) = \frac{1 + \cos(18x)}{2}.
\]
Substitute this identity back into the integral:
\[
\int_{-\pi}^{\pi} \cos^2(9x) \, dx = \int_{-\pi}^{\pi} \frac{1 + \cos(18x)}{2} \, dx.
\]
This becomes:
\[
\frac{1}{2} \int_{-\pi}^{\pi} (1 + \cos(18x)) \, dx = \frac{1}{2} \left( \int_{-\pi}^{\pi} 1 \, dx + \int_{-\pi}^{\pi} \cos(18x) \, dx \right).
\]
Calculate each integral separately.
1. The integral of a constant over \([-π, π]\):
\[
\int_{-\pi}^{\pi} 1 \, dx = x \Big|_{-\pi}^{\pi} = \pi - (-\pi) = 2\pi.
\]
2. The integral of \(\cos(18x)\) over a symmetric interval:
The integral of \(\cos(kx)\) from \([-a, a]\) is zero if \(k \neq 0\), since cosine is an even function and its values will cancel out.
By observation:
\[
\int_{-\pi}^{\pi} \cos(18x) \, dx = 0.
\]
Finally, plug these results back into the original equation:
\[
\frac{1}{2} (2\pi + 0) = \frac{1}{2} \cdot 2](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F678fef96-64be-4096-a74a-c4eb0a405ee7%2F8574f19a-39b9-4839-a657-02f41a609a80%2F3l6avk6_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
Evaluate the integral
\[
\int_{-\pi}^{\pi} \cos^2(9x) \, dx.
\]
**Explanation:**
The problem involves integrating the square of the cosine function with a multiple angle, \(9x\), over the symmetric interval \([-π, π]\).
A common technique to solve integrals of squared trigonometric functions is to use the power-reduction identity:
\[
\cos^2(\theta) = \frac{1 + \cos(2\theta)}{2}.
\]
In this case, substitute \(\theta = 9x\), so:
\[
\cos^2(9x) = \frac{1 + \cos(18x)}{2}.
\]
Substitute this identity back into the integral:
\[
\int_{-\pi}^{\pi} \cos^2(9x) \, dx = \int_{-\pi}^{\pi} \frac{1 + \cos(18x)}{2} \, dx.
\]
This becomes:
\[
\frac{1}{2} \int_{-\pi}^{\pi} (1 + \cos(18x)) \, dx = \frac{1}{2} \left( \int_{-\pi}^{\pi} 1 \, dx + \int_{-\pi}^{\pi} \cos(18x) \, dx \right).
\]
Calculate each integral separately.
1. The integral of a constant over \([-π, π]\):
\[
\int_{-\pi}^{\pi} 1 \, dx = x \Big|_{-\pi}^{\pi} = \pi - (-\pi) = 2\pi.
\]
2. The integral of \(\cos(18x)\) over a symmetric interval:
The integral of \(\cos(kx)\) from \([-a, a]\) is zero if \(k \neq 0\), since cosine is an even function and its values will cancel out.
By observation:
\[
\int_{-\pi}^{\pi} \cos(18x) \, dx = 0.
\]
Finally, plug these results back into the original equation:
\[
\frac{1}{2} (2\pi + 0) = \frac{1}{2} \cdot 2
Expert Solution
Step 1
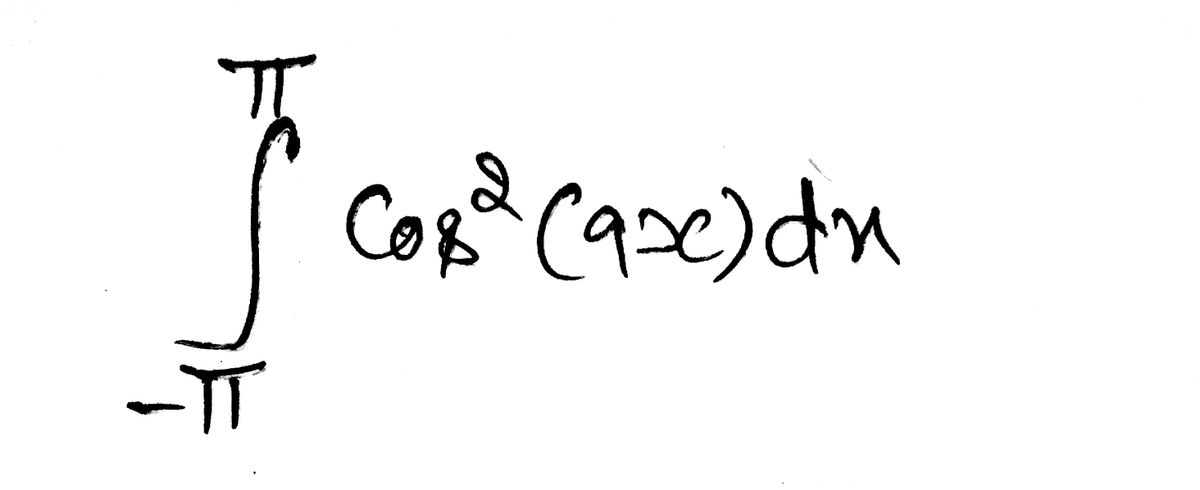
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning