Ionic Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium and ionic equilibrium are two major concepts in chemistry. Ionic equilibrium deals with the equilibrium involved in an ionization process while chemical equilibrium deals with the equilibrium during a chemical change. Ionic equilibrium is established between the ions and unionized species in a system. Understanding the concept of ionic equilibrium is very important to answer the questions related to certain chemical reactions in chemistry.
Arrhenius Acid
Arrhenius acid act as a good electrolyte as it dissociates to its respective ions in the aqueous solutions. Keeping it similar to the general acid properties, Arrhenius acid also neutralizes bases and turns litmus paper into red.
Bronsted Lowry Base In Inorganic Chemistry
Bronsted-Lowry base in inorganic chemistry is any chemical substance that can accept a proton from the other chemical substance it is reacting with.
![**Problem:**
The \( K_a \) of a monoprotic weak acid is 0.00485. What is the percent ionization of a 0.101 M solution of this acid?
**Solution:**
To find the percent ionization, use the formula:
\[
\text{Percent Ionization} = \left( \frac{[H^+]}{[HA]_0} \right) \times 100\%
\]
Where:
- \([H^+]\) is the concentration of hydrogen ions at equilibrium.
- \([HA]_0\) is the initial concentration of the acid.
Given:
- \( K_a = 0.00485 \)
- \([HA]_0 = 0.101 \, \text{M} \)
Assume \( x \) is the concentration of \( H^+ \) ionized from acid at equilibrium:
\[
K_a = \frac{x^2}{0.101 - x} \approx \frac{x^2}{0.101}
\]
Since \( K_a \) is small, assume \( x \ll 0.101 \):
\[
x^2 \approx K_a \times 0.101
\]
Solve for \( x \):
1. \( x^2 = 0.00485 \times 0.101 \)
2. \( x^2 = 0.000489485 \)
3. \( x = \sqrt{0.000489485} \)
4. \( x \approx 0.0221 \)
Calculate percent ionization:
\[
\text{Percent Ionization} = \left( \frac{0.0221}{0.101} \right) \times 100\% \approx 21.88\%
\]
The percent ionization of the acid in a 0.101 M solution is approximately 21.88%.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F8da5c625-81d8-4db3-9f61-2b28dd7af5ea%2F88a93a9b-93f5-4c90-a567-cd0e495007a6%2Fbt1k3zk_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
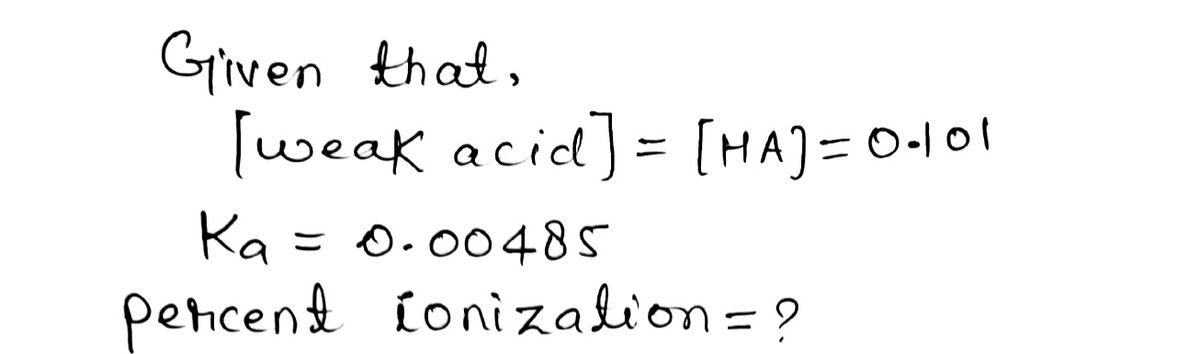
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









