{e, 9) € R² : 52. {(x,y) € R² : (y-x)(y+x) = 0} (y-x²)(y+x²) = 0}
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
100%
Only D52
![8
C. Find the following cardinalities.
29. |{{1}, {2, {3,4}},ø}|
30, |{{1,4},a,b, {{3,4}}, {Ø}}|
31. |{{{1}, {2, {3, 4}},Ø}}|
32. |{{{1,4},a,b, {{3,4}}, {ø}}|
33. |{x € Z: \x| < 10}|
The Ca.
34. |{x €N: \x| < 10}|
35. |{x € Z:x² < 10}|
36. |{x €N:x² < 10}|
37. 1{z €N:x2 <아}
38, |{x €N: 5x < 20}|
Th
exam
Fig
eler
D. Sketch the following sets of points in the x-y plane.
39. {(x, y):x€ [1,21,y € [1,2]}
40. {(x,y):xE [0, 1], y e [1,21}
41. {(x, y) : x € [-1, 1], y = 1}
42. {(2, y): x= 2,y € [0, 1]}
43. {(x,y): |2| = 2,y E [0, 1)}
44. {(x, x*) : x € R}
45. {(x, y) : #,y € R,x² + y² = 1}
46. {(x, y) : x,y € R,x² + y² s 1}
47. {(x, y) : x, y € R, y z x² – 1}
48. {(x, y) : x, y € R, x> 1}
49. {(x,x+ y) ;x € R, y € Z}
50. {x, 등): xeR,yEN}
51. {(x, y) e R² : (y – x)(y +x) = 0}
(52, {(x,y) e R² : (y–x²)(y + x²) = 0}
A
ele
1.2 The Cartesian Product
Given two sets A and B, it is possible to "multiply" them to produce a new
set denoted as Ax B. This operation is called the Cartesian product. To
understand it, we must first understand the idea of an ordered pair.
Definition 1.1 An ordered pair is a list (x, y) of two things x and y,
enclosed in parentheses and separated by a comma.
For example, (2. 4) is an oud](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fd06cff55-e1fa-4bcb-ab93-6fc7f7940672%2F8f02f70a-1df1-40bc-ba5c-15ec57aa275d%2Fibtymkv_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:8
C. Find the following cardinalities.
29. |{{1}, {2, {3,4}},ø}|
30, |{{1,4},a,b, {{3,4}}, {Ø}}|
31. |{{{1}, {2, {3, 4}},Ø}}|
32. |{{{1,4},a,b, {{3,4}}, {ø}}|
33. |{x € Z: \x| < 10}|
The Ca.
34. |{x €N: \x| < 10}|
35. |{x € Z:x² < 10}|
36. |{x €N:x² < 10}|
37. 1{z €N:x2 <아}
38, |{x €N: 5x < 20}|
Th
exam
Fig
eler
D. Sketch the following sets of points in the x-y plane.
39. {(x, y):x€ [1,21,y € [1,2]}
40. {(x,y):xE [0, 1], y e [1,21}
41. {(x, y) : x € [-1, 1], y = 1}
42. {(2, y): x= 2,y € [0, 1]}
43. {(x,y): |2| = 2,y E [0, 1)}
44. {(x, x*) : x € R}
45. {(x, y) : #,y € R,x² + y² = 1}
46. {(x, y) : x,y € R,x² + y² s 1}
47. {(x, y) : x, y € R, y z x² – 1}
48. {(x, y) : x, y € R, x> 1}
49. {(x,x+ y) ;x € R, y € Z}
50. {x, 등): xeR,yEN}
51. {(x, y) e R² : (y – x)(y +x) = 0}
(52, {(x,y) e R² : (y–x²)(y + x²) = 0}
A
ele
1.2 The Cartesian Product
Given two sets A and B, it is possible to "multiply" them to produce a new
set denoted as Ax B. This operation is called the Cartesian product. To
understand it, we must first understand the idea of an ordered pair.
Definition 1.1 An ordered pair is a list (x, y) of two things x and y,
enclosed in parentheses and separated by a comma.
For example, (2. 4) is an oud
Expert Solution
Step 1
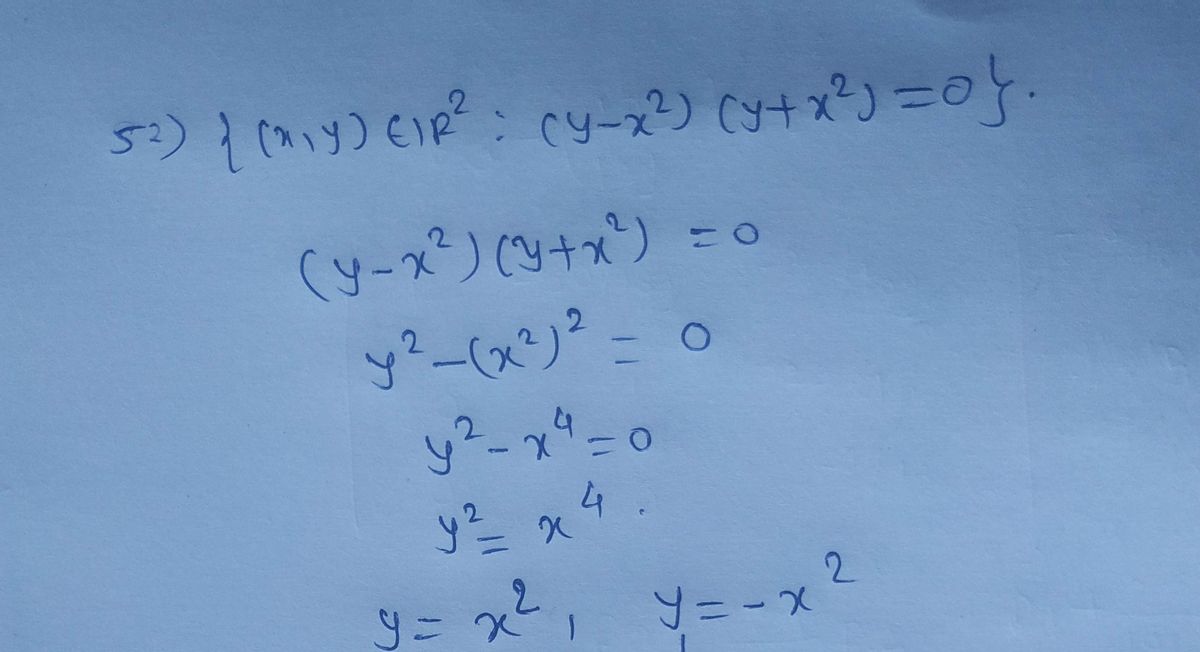
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

