Draw the structure of the expected organic product(s) formed in the following reactions including correct stereochemistry. If the product is racemic, write racemic or draw both isomers. Assume all reagents listed are present in excess unless otherwise noted. If no reaction occurs, state "no reaction".
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the organic compounds that are obtained in foods and living matters in the shape of sugars, cellulose, and starch. The general formula of carbohydrates is Cn(H2O)2. The ratio of H and O present in carbohydrates is identical to water.
Starch
Starch is a polysaccharide carbohydrate that belongs to the category of polysaccharide carbohydrates.
Mutarotation
The rotation of a particular structure of the chiral compound because of the epimerization is called mutarotation. It is the repercussion of the ring chain tautomerism. In terms of glucose, this can be defined as the modification in the equilibrium of the α- and β- glucose anomers upon its dissolution in the solvent water. This process is usually seen in the chemistry of carbohydrates.
L Sugar
A chemical compound that is represented with a molecular formula C6H12O6 is called L-(-) sugar. At the carbon’s 5th position, the hydroxyl group is placed to the compound’s left and therefore the sugar is represented as L(-)-sugar. It is capable of rotating the polarized light’s plane in the direction anticlockwise. L isomers are one of the 2 isomers formed by the configurational stereochemistry of the carbohydrates.
Draw the structure of the expected organic product(s) formed in the following reactions including correct stereochemistry. If the product is racemic, write racemic or draw both isomers. Assume all reagents listed are present in excess unless otherwise noted. If no reaction occurs, state "no reaction".

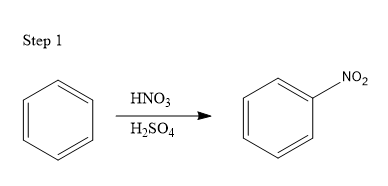
The given reaction is an example of an aromatic substitution reaction. The given series of reactions takes place in three steps:
In the first step, a benzene molecule reacts with nitric acid (HNO3) in the presence of sulphuric acid (H2SO4). This mixture is known as the nitrating mixture and the benzene molecule undergoes nitration reaction in which a nitro group gets attached to the benzene ring substituting one of the hydrogen atoms. The resultant product formed is nitrobenzene as shown below:
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images









