Discuss the long-term effects in a monopolistically competitive market if an existing firm is making profits or losses (). Use graphs to illustrate your explanations.

Monopolistic competition is a blend of perfect competition and monopoly. Monopolistic competition refers to a market structure in which there are many sellers of a heterogeneous or differentiated products and entry into or exit from the industry is rather easy in the long run.
A monopolistic competitive firm faces a negatively sloped demand curve because the firm produces differentiated product. But the demand curve is highly price elastic because there are many close substitutes for the product. Since the demand curve facing a monopolistic competitor is negatively sloped, the marginal revenue curve is below it. As for the firms under any type of market structure, the best level of output for monopolistically competitive firm in the short run is where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, provided that the price exceeds the average variable cost. This is shown in the left panel of the following figure.
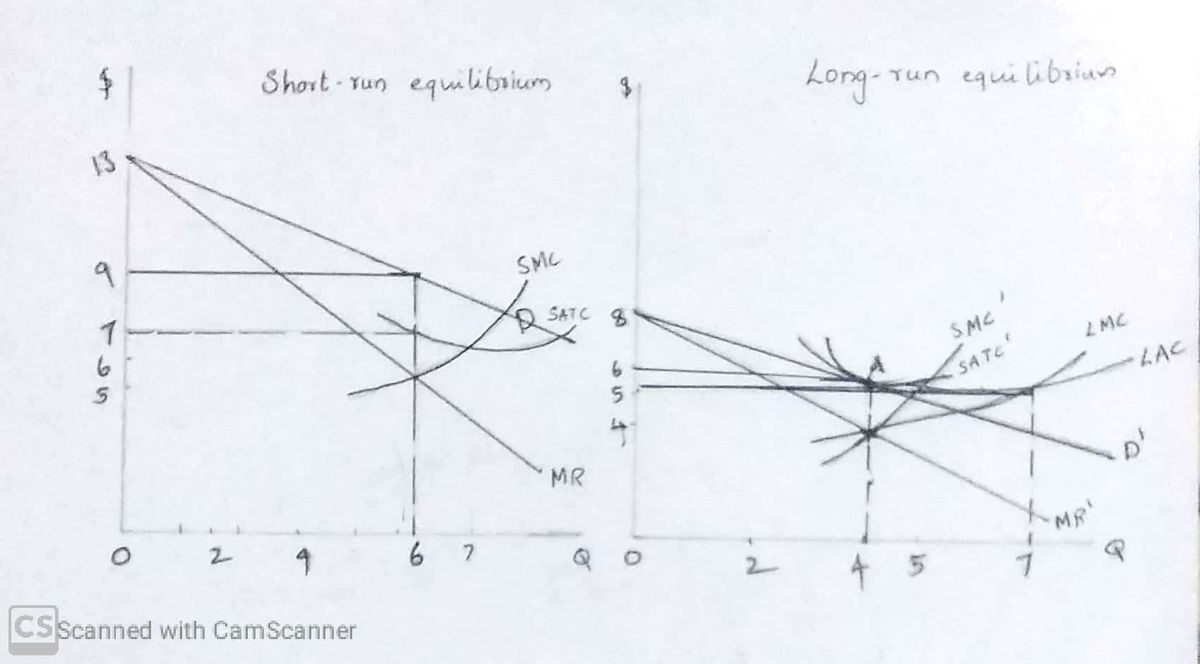
In the figure the best level of output for the firm in the short run is 6 units at which MR=SMC. To sell the best output the firm charges a price of $9 per unit. At this price the firm earns a profit of $2. As in the case of perfect competition or monopoly, the monopolistic competitor can earn profit, break even or incur loss in the short run.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









