Determine the resultant R. Compute magnitude, sense and angle of inclination with horizontal x.
Determine the resultant R. Compute magnitude, sense and angle of inclination with horizontal x.
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Determine the resultant R. Compute magnitude, sense and angle of inclination with horizontal x.

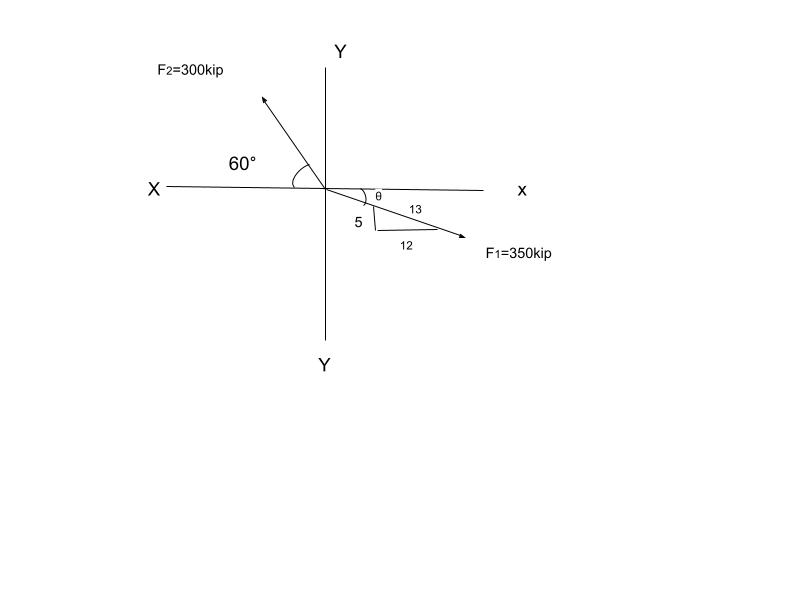
Transcribed Image Text:The image is a vector diagram illustrating two forces acting at a point, labeled \( O \). It features a Cartesian coordinate system with positive and negative axes: X(+) and X(-), Y(+) and Y(-).
- **Force \( F_1 \):**
- Magnitude: 350 kips
- Direction: Along a vector that is resolved into a right triangle with sides proportional to 5, 12, and 13, suggesting its direction can be calculated using the ratio of these sides.
- **Force \( F_2 \):**
- Magnitude: 300 kips
- Direction: 60 degrees from the negative X-axis.
The forces are shown as arrows originating from point \( O \), with \( F_1 \) pointing towards the first quadrant and \( F_2 \) pointing towards the second quadrant, at a specified angle from the negative X-axis. The diagram visually represents the resolution of forces and may be used to analyze the vector components along the X and Y axes.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Given data
force F1=350kip
force F2=300kip
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning