
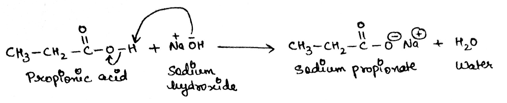
Carboxylic acids consists an acidic proton which is attached to oxygen atom. So, on reaction of carboxylic acid with sodium hydroxide NaOH, hydroxide ion, OH- takes up the acidic proton from carboxylic acid and formation of sodium salt of carboxylate ion takes place with the removal of a water molecule.
When the given propionic acid reacts with NaOH, hydroxide ions takes proton from propionic acid and sodium salt of carboxylate ions is formed with a molecule of water.
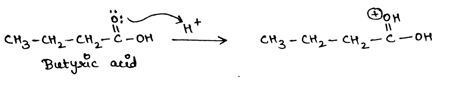
When a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of acid catalyst, formation of an ester takes place. In the first step, carbonyl oxygen of given butyric acid takes up proton from acid and carbonyl oxygen attains positive charge.
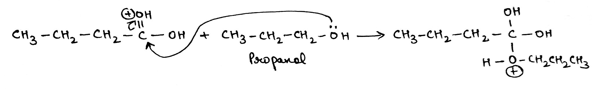
In the next step, lone pair of oxygen atom of given propanol attacks on electrophilic carbonyl carbon of butyric acid and double bond between carbonyl carbon and carbonyl oxygen of butyric acid breaks down by providing electron density to oxygen atom.
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 6 images









