1 Chemical Foundations 2 Atomic Structure And Periodicity 3 Bonding: General Concepts 4 Molecular Structure And Orbitals 5 Stoichiometry 6 Types Of Chemical Reactions And Solution Stoichiometry 7 Chemical Energy 8 Gases 9 Liquids And Solids 10 Properties Of Solutions 11 Chemical Kinetics 12 Chemical Equilibrium 13 Acids And Bases 14 Acid- Base Equilibria 15 Solubility And Complex Lon Equilibria 16 Spontaneity, Entropy, And Free Energy 17 Electrochemistry 18 The Nucleus: A Chemist's View 19 The Representative Elements 20 Transition Metals And Coordination Chemistry 21 Organic And Biological Molecules Chapter7: Chemical Energy
Chapter Questions Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define the following terms: potential energy, kinetic energy, path-dependent function, state... Problem 2RQ: Consider the following potential energy diagrams for two different reactions. Which plot represents... Problem 3RQ: What is the first law of thermodynamics? How can a system change its internal energy, E? What are... Problem 4RQ: When a gas expands, what is the sign of w? Why? When a gas contracts, what is the sign of w? Why?... Problem 5RQ Problem 6RQ: High-quality audio amplifiers generate large amounts of heat. To dissipate the heat and prevent... Problem 7RQ: Explain how calorimetry works to calculate H or E for a reaction. Does the temperature of the... Problem 8RQ: What is Hesss law? When a reaction is reversed, what happens to the sign and magnitude of H for that... Problem 9RQ: Define the standard enthalpy of formation. What are standard states for elements and for compounds?... Problem 1ALQ Problem 2ALQ Problem 3ALQ: A fire is started in a fireplace by striking a match and lighting crumpled paper under some logs.... Problem 4ALQ: Liquid water turns to ice. Is this process endothermic or exothermic? Explain what is occurring... Problem 5ALQ Problem 6ALQ Problem 7ALQ: Consider 5.5 L of a gas at a pressure of 3.0 atm in a cylinder with a movable piston. The external... Problem 8ALQ: Explain why oceanfront areas generally have smaller temperature fluctuations than inland areas. Problem 9ALQ: Hesss law is really just another statement of the first law of thermodynamics. Explain. Problem 10ALQ Problem 11Q Problem 12Q Problem 13Q: Assuming gasoline is pure C8H18(l), predict the signs of q and w for the process of combusting... Problem 14Q Problem 15Q: The enthalpy change for the reaction CH4(g)+2O2(g)CO2(g)+2H2O(l) is 891 kJ for the reaction as... Problem 16Q: For the reaction HgO(s)Hg(l)+12O2(g),H=+90.7KJ: a. What quantity of heat is required to produce 1... Problem 17Q Problem 18Q: The enthalpy change for a reaction is a state function and it is an extensive property. Explain. Problem 19Q: Standard enthalpies of formation are relative values. What are Hfvalues relative to? Problem 20Q: The combustion of methane can be represented as follows: a. Use the information given above to... Problem 21Q Problem 22Q Problem 23Q Problem 24Q Problem 25E Problem 26E Problem 27E: Consider the following diagram when answering the questions below. a. Compare balls A and B in terms... Problem 28E: Consider the accompanying diagram. Ball A is allowed to fall and strike ball B. Assume that all of... Problem 29E: A gas absorbs 45 kJ of heat and does 29 kJ of work. Calculate E. Problem 30E: A system releases 125 kJ of heat while 104 kJ of work is done on it. Calculate E. Problem 31E: Calculate E for each of the following. a. q = 47 kJ, w = + 88 kJ b. q = +82 kJ, w = 47 kJ c. q = +... Problem 32E: A system undergoes a process consisting of the following two steps: Step 1: The system absorbs 72 J... Problem 33E: If the internal energy of a thermodynamic system is increased by 300. J while 75 J of expansion work... Problem 34E: Calculate the internal energy change for each of the following. a. One hundred (100.) joules of work... Problem 35E: A sample of an ideal gas at 15.0 atm and 10.0 L is allowed to expand against a constant external... Problem 36E Problem 37E: Consider a mixture of air and gasoline vapor in a cylinder with a piston. The original volume is 40.... Problem 38E: As a system increases in volume, it absorbs 52.5 J of energy in the form of heat from the... Problem 39E: A balloon filled with 39.1 moles of helium has a volume of 876 L at 0.0C and 1.00 atm pressure. The... Problem 40E Problem 41E: One of the components of polluted air is NO. It is formed in the high-temperature environment of... Problem 42E Problem 43E: Are the following processes exothermic or endothermic? a. When solid KBr is dissolved in water, the... Problem 44E: Are the following processes exothermic or endothermic? a. the combustion of gasoline in a car engine... Problem 45E: The overall reaction in a commercial heat pack can be represented as 4Fe(s)+3O2(g)2Fe2O3(s)H=1652KJ... Problem 46E: Consider the following reaction: 2H2(g)+O2(g)2H2O(l)H=572KJ a. How much heat is evolved for the... Problem 47E: Consider the combustion of propane: C3H8(g)+5O2(g)3CO2(g)+4H2O(l)H=2221KJ Assume that all the heat... Problem 48E: Consider the following reaction: CH4(g)+2O2(g)CO2(g)+2H2O(l)H=891KJ Calculate the enthalpy change... Problem 49E Problem 50E: The specific heat capacity of silver is 0.24 J/Cg. a. Calculate the energy required to raise the... Problem 51E: A 500-g sample of one of the substances listed in Table 7-1 was heated from 25.2C to 55.1C,... Problem 52E Problem 53E: A 30.0-g sample of water at 280. K is mixed with 50.0 g water at 330. K. Calculate the final... Problem 54E: A biology experiment requires the preparation of a water bath at 37.0C (body temperature). The... Problem 55E: A 5.00-g sample of aluminum pellets (specific heat capacity = 0.89 J/C g) and a 10.00-g sample of... Problem 56E: Hydrogen gives off 120. J/g of energy when burned in oxygen, and methane gives off 50. J/g under the... Problem 57E Problem 58E: A 110.-g sample of copper (specific heat capacity = 0.20 J/C g) is heated to 82.4C and then placed... Problem 59E: In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 50.0 mL of 0.100 M AgNO3 and 50.0 mL of 0.100 M HCl are mixed to yield... Problem 60E: In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 100.0 mL of 1.0 M NaOH and 100.0 mL of 1.0 M HCI are mixed. Both... Problem 61E: A coffee-cup calorimeter initially contains 125 g water at 24.2C. Potassium bromide (10.5 g), also... Problem 62E: In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 1.60 g NH4NO3 is mixed with 75.0 g water at an initial temperature of... Problem 63E: Consider the dissolution of CaCl2: CaCl2(s)Ca2+(aq)+2Cl(aq)H=81.5KJ An 11.0-g sample of CaCl2 is... Problem 64E: Consider the reaction 2HCl(aq)+Ba(OH)2(aq)BaCl2(aq)+2H2O(l)H=118KJ Calculate the heat when 100.0 rnL... Problem 65E: The heat capacity of a bomb calorimeter was determined by burning 6.79 g methane (energy of... Problem 66E: The combustion of 0.1584 g benzoic acid increases the temperature of a bomb calorimeter by 2.54C.... Problem 67E: The enthalpy of combustion of solid carbon to form carbon dioxide is 393.7 KJ/mol carbon, and the... Problem 68E: Combustion reactions involve reacting a substance with oxygen. When compounds containing carbon and... Problem 69E: Given the following data calculate H for the reaction On the basis of the enthalpy change, is this a... Problem 70E: Given the following data... Problem 71E Problem 72E: Calculate H for the reaction 2NH3(g)+12O2(g)N2H4(l)+H2O(l) given the following data:... Problem 73E: Given the following data... Problem 74E: Given the following data... Problem 75E: Give the definition of the standard enthalpy of formation for a substance. Write separate reactions... Problem 76E: Write reactions for which the enthalpy change will be a. Hf for solid aluminum oxide. b. the... Problem 77E Problem 78E: Use the values of Hf in Appendix 4 to calculate H for the following reactions. (See Exercise 77 .)... Problem 79E: The Ostwald process for the commercial production of nitric acid from ammonia and oxygen involves... Problem 80E: Calculate H for each of the following reactions using the data in Appendix 4:... Problem 81E: The reusable booster rockets of the space shuttle use a mixture of aluminum and ammonium perchlorate... Problem 82E: The space shuttle Orbiter utilizes the oxidation of methylhydrazine by dinitrogen tetroxide for... Problem 83E: Consider the reaction 2ClF3(g)+2NH3(g)N2(g)+6HF(g)+Cl2(g)H=1196KJ Calculate H for CIF3(g). Problem 84E: The standard enthalpy of combustion of ethene gas, C2H4(g), is 1411.1 kJ/mol at 298 K. Given the... Problem 85E: Water gas is produced from the reaction of steam with coal: C(s)+H2O(g)H2(g)+CO(g) Assuming that... Problem 86E Problem 87E Problem 88E Problem 89E: Some automobiles and buses have been equipped to bum propane (C3H8). Compare the amounts of energy... Problem 90E: The complete combustion of acetylene, C2H2(g), produces 1300. kJ of energy per mole of acetylene... Problem 91AE Problem 92AE: One way to lose weight is to exercise! Walking briskly at 4.0 miles per hour for an hour consumes... Problem 93AE: Three gas-phase reactions were run in a constant-pressure piston apparatus as shown in the following... Problem 94AE: Nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen gas to form ammonia gas .Consider the reaction between nitrogen... Problem 95AE: Combustion of table sugar produces CO2(g) and H2O( l). When 1.46 g table sugar is combusted in a... Problem 96AE Problem 97AE: Consider the following cyclic process carried out in two steps on a gas: Step 1: 45 J of heat is... Problem 98AE: Calculate H for the reaction 2K(s)+2H2O(l)2KOH(aq)+H2(g) A 5.00-g chunk of potassium is dropped into... Problem 99AE: The enthalpy of neutralization for the reaction of a strong acid with a strong base is 56 kJ/mol... Problem 100AE Problem 101AE: If a student performs an endothermic reaction in a calorimeter, how does the calculated value of H... Problem 102AE: In a bomb calorimeter, the reaction vessel is surrounded by water that must be added for each... Problem 103AE: The bomb calorimeter in Exercise 102 is filled with 987 g water. The initial temperature of the... Problem 104AE Problem 105AE: Consider the following equations: 3A+6B3DH=403KJ/molE+2FAH=105.2KJ/molCE+3DH=64.8KJ/mol Suppose the... Problem 106AE Problem 107AE: At 298 K, the standard enthalpies of formation for C2H2(g) and C6H6(l) are 227 kJ/mol and 49 kJ/mol,... Problem 108AE Problem 109AE: A sample of nickel is heated to 99.8C and placed in a coffee-cup calorimeter containing 150.0 g... Problem 110AE: Quinone is an important type of molecule that is involved in photosynthesis. The transport of... Problem 111AE: Calculate H for each of the following reactions, which occur in the atmosphere. a.... Problem 112AE: Compare your answers from parts a and b of Exercise 69 of Chapter 3 with H values calculated for... Problem 113AE: Compare your answer from Exercise 72 of Chapter 3 to the H value calculated from standard enthalpies... Problem 114CWP: Consider a balloon filled with helium at the following conditions. 313 g He 1.00 atm 1910. L Molar... Problem 115CWP Problem 116CWP Problem 117CWP Problem 118CWP: A swimming pool, 10.0 m by 4.0 m, is filled with water to a depth of 3.0 m at a temperature of... Problem 119CWP Problem 120CWP: Calculate H for the reaction N2H4(l)+O2(g)N2(g)+2H2O(l) given the following data: Equation H(KJ)... Problem 121CWP: Which of the following substances have an enthalpy of formation equal to zero? a. Cl2(g) b. H2(g) c.... Problem 122CP: Consider 2.00 moles of an ideal gas that are taken from state A (PA = 2.00 atm, vA = 10.0 L) to... Problem 123CP: For the process H2O(l)H2O(g) at 298 K and 1.0 atm, H is more positive than E by 2.5 kJ/mol. What... Problem 124CP: The sun supplies energy at a rate of about 1.0 kilowatt per square meter of surface area (1 watt = 1... Problem 125CP Problem 126CP: The standard enthalpies of formation for S(g), F(g), SF4(g), and SF6(g) are +278.8, +79.0, 775, and... Problem 127CP: Use the following standard enthalpies of formation to estimate the N-H bond energy in ammonia: N(g),... Problem 128CP: The standard enthalpy of formation for N2H4(g) is 95.4 kJ/mol. Use this and the data in Exercise 127... Problem 129CP: The standard enthalpy of formation for NO(g) is 90. kJ/mol. Use this and the values for the O 9 O... Problem 130CP: A piece of chocolate cake contains about 400 calories. A nutritional calorie is equal to 1000... Problem 131CP: You have a l.00-mole sample of water at 30.C and you heat it until you have gaseous water at 140.C.... Problem 132CP: A 500.0-g sample of an element at 195C is dropped into an ice--water mixture; 109.5 g ice melts and... Problem 133IP: A cubic piece of uranium metal (specific heat capacity = 0.117 J/C g) at 200.0C is dropped into... Problem 134IP: On Easter Sunday, April 3, 1983, nitric acid spilled from a tank car near downtown Denver, Colorado.... Problem 135IP: Using data from Chapter 2, calculate the change in energy expected for each of the following... Problem 136IP: In Exercise 89 in Chapter 3, the Lewis structures for benzene (C6H6) were drawn. Using one of the... Problem 137MP: A gaseous hydrocarbon reacts completely with oxygen gas to form carbon dioxide and water vapour.... Problem 134IP: On Easter Sunday, April 3, 1983, nitric acid spilled from a tank car near downtown Denver, Colorado....
Related questions
Concept explainers
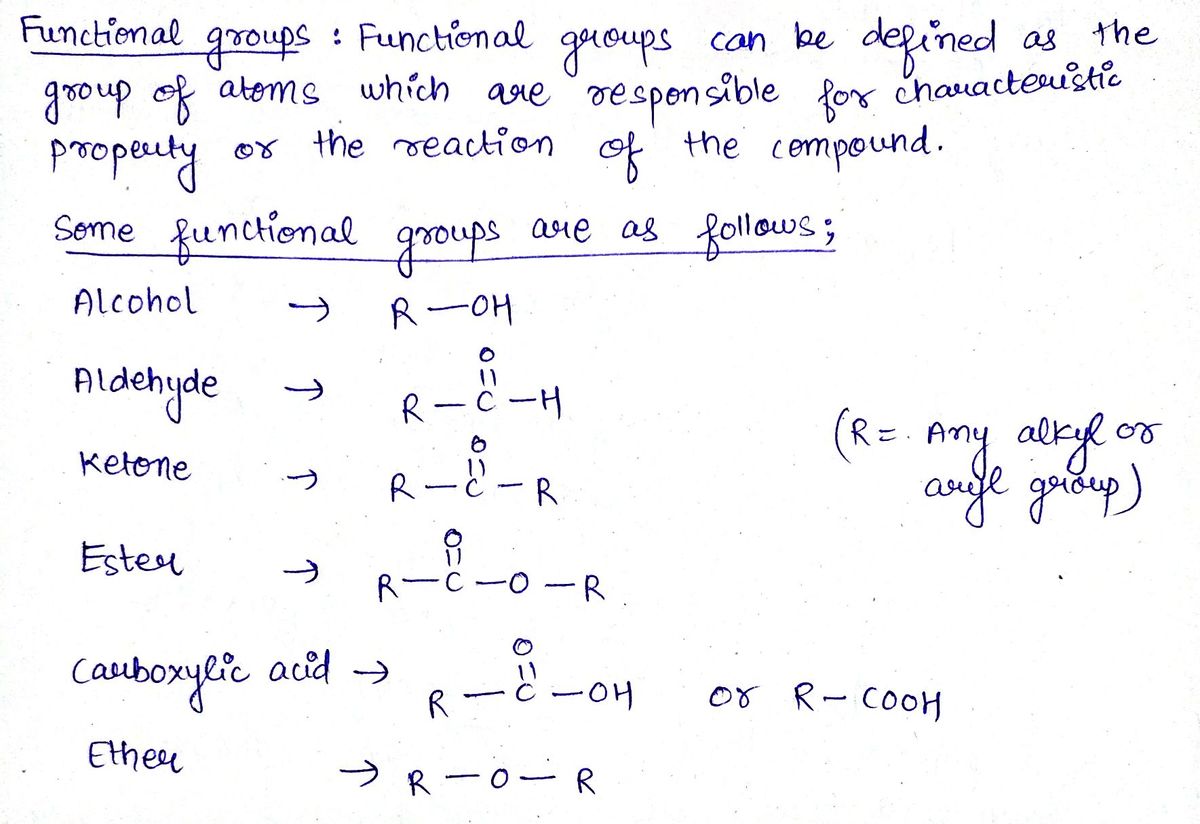
Determine the functional groups of the following
Transcribed Image Text: g.
J.
m
d.
a.
P.
IZ
OH
CHO
CH₂CH₂CH=CH₂
S
S
b.
e
h.
k.
n
OH
O
NH₂
9.
C.
f
OH
i.
1
O.
COOH
SH
O=
O
OH
Definition Definition Group of atoms that shape the chemical characteristics of a molecule. The behavior of a functional group is uniform in undergoing comparable chemical reactions, regardless of the other constituents of the molecule. Functional groups aid in the classification and anticipation of reactivity of organic molecules.
Expert Solution
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images