Describe how action potentials are propagated and each step of action potential , be sure to know how Na and K channels, pumps operate, what is the difference between open, closed and inactivated channels and why
Describe how action potentials are propagated and each step of action potential , be sure to know how Na and K channels, pumps operate, what is the difference between open, closed and inactivated channels and why
The action potential is defined as sudden and fast propagating change taking place in the cell membrane's resting potential.
Propagation of action potential:
Resting membrane potential: The resting phase of the axon when no stimulus is generated.
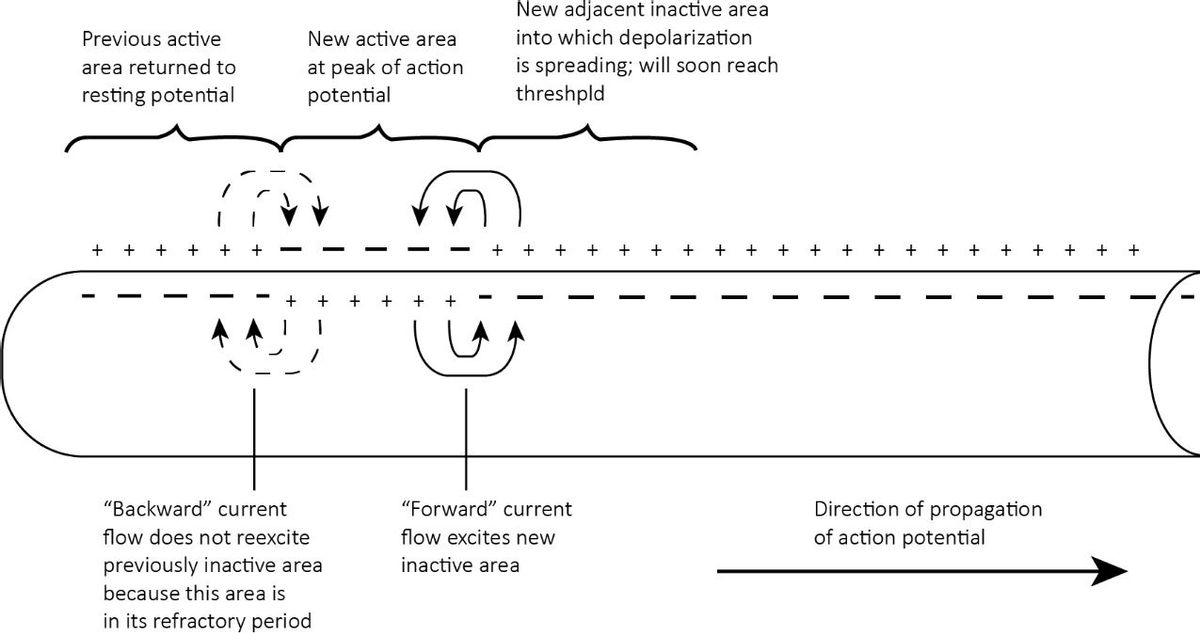
Depolarization: As the action potential will go down the axon's length, it is propagated due to the opening of more voltage-gated Na+ channels as the depolarization will spread. As the Na+ will move a short distance along the cellular membrane, the positive charge will depolarize more of the cellular membrane, and on reaching threshold there will be a generation of an action potential.
Repolarization: The increased positive charge inside the cell due to sodium ions will cause potassium channels to open. Thus, K+ ions will now move down the electrochemical gradient present out of the cell. As the K+ moves out of the cell, the membrane's potential falls and starts approaching the resting potential.
The differences between an open channel, a closed channel and inactivated channel are:
Open channels allow the flow of ions through it depending on the cell requirements.
Closed channels are those that do not allow ions flow due to a lack of requirements in the cell.
Inactivated channels are a type of closed channel which do not allow ions flow due to conformational change in the channel protein leading to channel inactivation.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









