Density of Water In this part, we will try to measure or calculate the density of water. As we have learned in the lecture, the density of any matter will be the ratio of the mass of the given matter and the volume of the matter. We will have to obtain the data for the mass and the volume of that given amount of water. We will use a rectangle container for this purpose. If we measure the length, the width of the container, and if we pour the water in the container, we can calculate the volume of the water. To get the mass of the water, we will measure the mass of the empty container first, we will then measure the mass of the container with the water inside. The difference of this two mass will be the net mass of the water that we are interested. We will do three trials. We will just put different amount of water in the container. Different amount of water will give you different height, but the length and the width of the container is the same. Since this is a virtual lab, I have done all the measurements. You need go through those procedure and then calculate all the missing numbers in Table 2.3. The followings are the actual procedure to obtain those data.
Part C: Density of Water
In this part, we will try to measure or calculate the density of water. As we have learned
in the lecture, the density of any matter will be the ratio of the mass of the given matter
and the volume of the matter. We will have to obtain the data for the mass and the volume
of that given amount of water. We will use a rectangle container for this purpose. If we measure
the length, the width of the container, and if we pour the water in the container, we can calculate
the volume of the water. To get the mass of the water, we will measure the mass of the empty
container first, we will then measure the mass of the container with the water inside. The difference
of this two mass will be the net mass of the water that we are interested.
We will do three trials. We will just put different amount of water in the container. Different amount of water will give you different height, but the length and the width of the container is the same.
Since this is a virtual lab, I have done all the measurements. You need go through those procedure and then calculate all the missing numbers in Table 2.3. The followings are the actual procedure to obtain those data.
1. You will be given a straight-sided, rectangular containers. Measure the length, width, and height
of the container (Assume the thickness of the container is negligible.). Record these
measurements in Table 2.3 in rows 1, 2, and 3. Calculate and record the volume of each container
in row 4 of the data table. Volume=Length x Width x Height.
2. Measure and record the mass of empty container in row 5 of the table. Measure and record the
mass of each container with different amount of water inside. Record each mass of container with
water in row 6 of the table.Calculate and record the net mass of the water in each container (mass
of container plus water minusmass of empty container, or row 6 minus row 5 for each container).
Record the net mass of the water in row 7 of the data table.
3. Use a graduated cylinder to measure the volume of water in the three situation. Be sure
to get all the water into the graduated cylinder. Record the water volume of each container in
milliliters (mL) in row 8 of the table.
4. Calculate the ratio of cubic centimeters (cm3) to mL for each container by dividing the volume in
cubic centimeters (row 4 ) by the volume in milliliters (row 8). Record your findings in the
table.
5. Calculate the ratio of net mass per unit volume for each case by dividing the mass in grams (row
7 ) by the volume in mL (row 8 ). Record your results in the table.
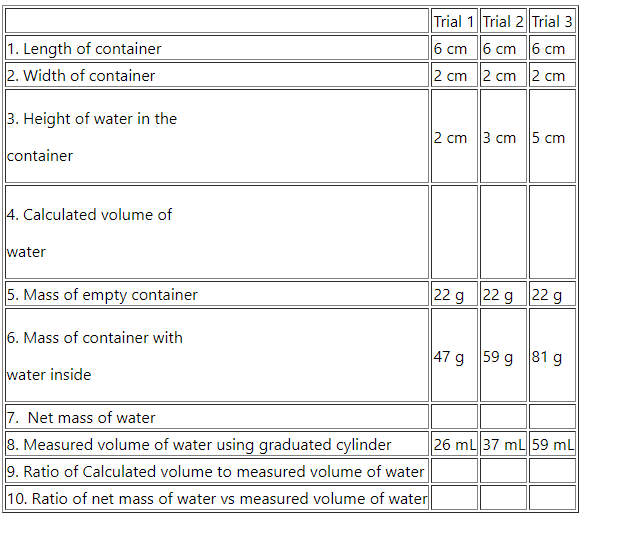
Table 2.3 Mass, Volume, and Density of water
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | Trial 3 | |
| 1. Length of container | 6 cm | 6 cm | 6 cm |
| 2. Width of container | 2 cm | 2 cm | 2 cm |
|
3. Height of water in the container |
2 cm | 3 cm | 5 cm |
|
4. Calculated volume of water |
|||
| 5. Mass of empty container | 22 g | 22 g | 22 g |
|
6. Mass of container with water inside |
47 g | 59 g | 81 g |
| 7. Net mass of water | |||
| 8. Measured volume of water using graduated cylinder | 26 mL | 37 mL | 59 mL |
| 9. Ratio of Calculated volume to measured volume of water | |||
| 10. Ratio of net mass of water vs measured volume of water |
Given:
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









