De Morgan's law
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
Consider the Venn diagram below. Illustrate the other De Morgan's law by selecting the region(s) corresponding to Ac ∪ Bc. (Select all that apply.)

Transcribed Image Text:The image is a Venn diagram consisting of three overlapping circles labeled \(A\), \(B\), and \(C\), within a larger rectangle labeled \(U\). Each circle represents a set, and the rectangle represents the universal set.
- **Circle A**: Represents set \(A\).
- **Circle B**: Represents set \(B\).
- **Circle C**: Represents set \(C\).
The overlaps between the circles represent the intersections of the sets:
- The area where circles \(A\) and \(B\) overlap represents the intersection \(A \cap B\).
- The area where circles \(A\) and \(C\) overlap represents the intersection \(A \cap C\).
- The area where circles \(B\) and \(C\) overlap represents the intersection \(B \cap C\).
- The central area where all three circles overlap represents the intersection \(A \cap B \cap C\).
The space outside the circles but inside the rectangle \(U\) represents elements that are in the universal set but not in sets \(A\), \(B\), or \(C\). This diagram is often used to illustrate relationships between different groups or categories.

Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a Venn diagram within a universal set \( U \), represented as a rectangle. It includes two intersecting circles labeled \( A \) and \( B \):
- The universal set \( U \) contains all possible elements in this context.
- Circle \( A \) represents a set of elements.
- Circle \( B \) represents another set of elements, which intersects with set \( A \).
The expression at the top left, \( A^c \cup B^c \), indicates the union of the complements of sets \( A \) and \( B \). This is equivalent to the shaded region outside both circles \( A \) and \( B \).
Check marks are visible in the following locations:
- Outside the circles \( A \) and \( B \) but inside the rectangle \( U \).
- In the intersection of \( A \) and \( B \) (middle section).
The areas with check marks indicate regions included in the set expression \( A^c \cup B^c \), whereas unchecked areas represent excluded regions.
Expert Solution
Step 1
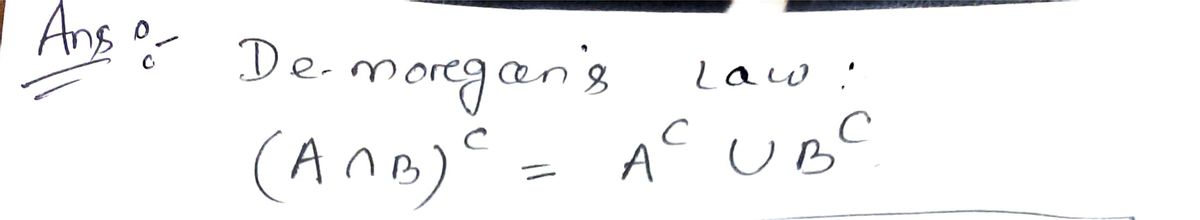
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

