Data Table n 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 μ= 0.00031 M (g) fexp= 260 2 240 S 5 9 50 9 35 kg/m L= 105 65 2m = 58.4 H₂ 9 M (kg) 0.00031 x 0.973 0.260 Ks 0.240 kg 0-105 ку 0.65 kg 0.50 ks 0.35 kg cm= 200 m M 9.81 T, Mg (N) 2 (cm) 2.548 2.352 1.029 6.37 4.90 3.43 Slope= fexp= Slope height = 19 x 0.27 -6.973 / Vi base 17 * 0.31 Calculation Table 200 cm 100 cm 800 cm 670cm 133 cm 3 570 cm 0.973 / λ (m) 58.4 H₂ 222 =2 1.596 222=1.33 1.533 1 0.8 0.67 √Ts (VN) 0.57 % Error= 1.014 1. Using at least 75% of the graph paper, make a graph with λ on Y axis and √T, on the X axis. 2. Draw a best fit line (a line that doesn't hit any data points but rather goes in between data points) and calculate the slope by picking two points exactly on the best fit line, do not use data points to calculate slope. Show your calculation to get credit. Record the slope of the best fit line in Data Table. 0.798 0.7 3. According to equation (4), A should be linearly proportional to √T, with as a slope. S√√μ Equate your value obtained for slope to and solve for the unknown frequency f. Record this value in Data Table as fexp. S√√μ 0.585
Data Table n 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 μ= 0.00031 M (g) fexp= 260 2 240 S 5 9 50 9 35 kg/m L= 105 65 2m = 58.4 H₂ 9 M (kg) 0.00031 x 0.973 0.260 Ks 0.240 kg 0-105 ку 0.65 kg 0.50 ks 0.35 kg cm= 200 m M 9.81 T, Mg (N) 2 (cm) 2.548 2.352 1.029 6.37 4.90 3.43 Slope= fexp= Slope height = 19 x 0.27 -6.973 / Vi base 17 * 0.31 Calculation Table 200 cm 100 cm 800 cm 670cm 133 cm 3 570 cm 0.973 / λ (m) 58.4 H₂ 222 =2 1.596 222=1.33 1.533 1 0.8 0.67 √Ts (VN) 0.57 % Error= 1.014 1. Using at least 75% of the graph paper, make a graph with λ on Y axis and √T, on the X axis. 2. Draw a best fit line (a line that doesn't hit any data points but rather goes in between data points) and calculate the slope by picking two points exactly on the best fit line, do not use data points to calculate slope. Show your calculation to get credit. Record the slope of the best fit line in Data Table. 0.798 0.7 3. According to equation (4), A should be linearly proportional to √T, with as a slope. S√√μ Equate your value obtained for slope to and solve for the unknown frequency f. Record this value in Data Table as fexp. S√√μ 0.585
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question
Hello, based on the information provided can you please help me do the % error on the table in the right

Transcribed Image Text:Data Table
n
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
μ=
0.00031
M (g)
kg/m L=
fexp=
260 2
240 9
105 5
65
9
50 9
35
2m
= 58.4 H₂
9
M (kg)
√0.00031 x 0.973
0.260 Ks
0240 kg
0-105 ка
0.65 kg
0.50 ks
0.35 kg
cm=
200
m
M
9.81
T, Mg (N) 2 (cm)
2.548
2.352
1.029
6.37
4.90
3.43
Slope=
fexp=
Slope height = 19 × 0.27 -6.973 / Vi
base
17 x 0.31
Calculation Table
200 cm
100 cm
800 cm
670cm
133 cm 3
570 cm
0.973 /
λ (m)
58.4 H₂
222 =2
1.596
222=1.33 1.533
I
0.8
0.67
√Ts (VN)
0.57
% Error=
1.014
1. Using at least 75% of the graph paper, make a graph with λ on Y axis and √T, on the X axis.
2. Draw a best fit line (a line that doesn't hit any data points but rather goes in between data
points) and calculate the slope by picking two points exactly on the best fit line, do not use
data points to calculate slope. Show your calculation to get credit. Record the slope of the
best fit line in Data Table.
0.798
0.7
3. According to equation (4), A should be linearly proportional to √T, with
as a slope.
S√√μ
Equate your value obtained for slope to and solve for the unknown frequency f. Record
f√μ
this value in Data Table as fexp.
0.585
Expert Solution
Step 1: Determine the given informations
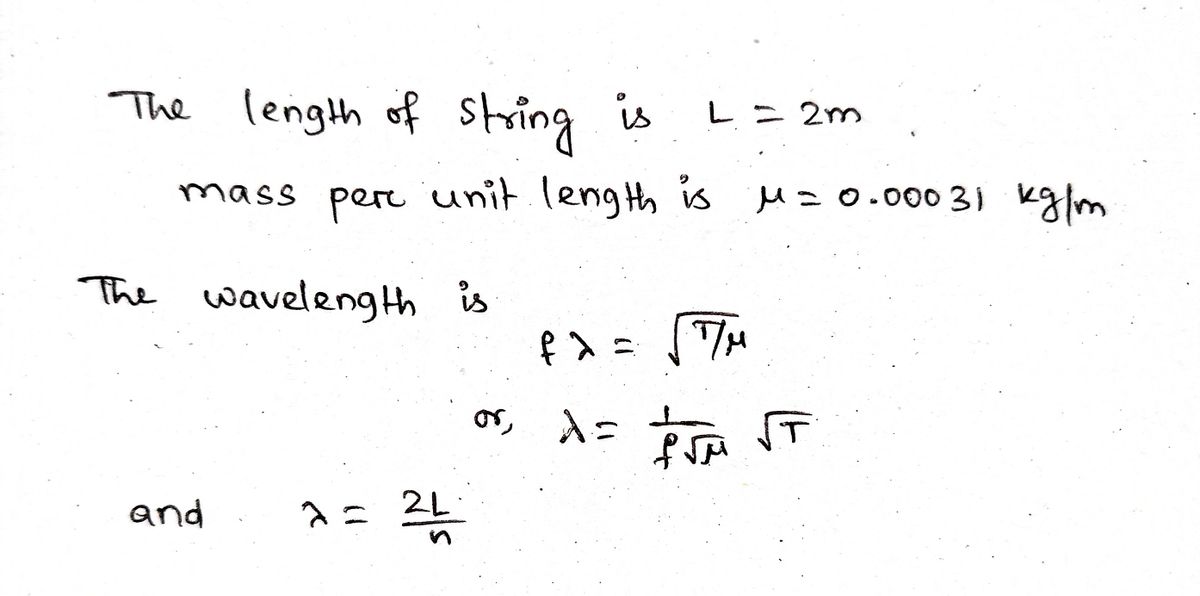
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON