d. Use the summary statistics, part c, to find a 90% confidence interval for the true mean differ- ence (“lst Hole" minus "2nd Hole") in THM measurements. e. Interpret the interval, part d. Can the geologists con- clude that there is no evidence of a difference in the true THM means of all original holes and their twin holes drilled at the mine? Location 1st Hole 2nd Hole 1 2 3 5.5 11.0 5.7 11.2 6.0 5.9 8.2 10.0 4 5.6 9.3 7.9 10.1 7.4 7.0 7 8.4 9.0 8 9 7.0 9.2 6.0 8.1 10 10.0 8.1 10.4 11 8.3 8.6 10.5 12 13 14 15 5.5 10.0 7.0 11.2
d. Use the summary statistics, part c, to find a 90% confidence interval for the true mean differ- ence (“lst Hole" minus "2nd Hole") in THM measurements. e. Interpret the interval, part d. Can the geologists con- clude that there is no evidence of a difference in the true THM means of all original holes and their twin holes drilled at the mine? Location 1st Hole 2nd Hole 1 2 3 5.5 11.0 5.7 11.2 6.0 5.9 8.2 10.0 4 5.6 9.3 7.9 10.1 7.4 7.0 7 8.4 9.0 8 9 7.0 9.2 6.0 8.1 10 10.0 8.1 10.4 11 8.3 8.6 10.5 12 13 14 15 5.5 10.0 7.0 11.2
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
d and e

Transcribed Image Text:d. Use the summary statistics, part c, to find a 90%
confidence interval for the
true
mean
differ-
ence (“Ist Hole" minus "2nd Hole") in THM
measurements.
e. Interpret the interval, part d. Can the geologists con-
clude that there is no evidence of a difference in the
true THM means of all original holes and their twin
holes drilled at the mine?
Location
1st Hole
2nd Hole
1
2
5.5
11.0
5.9
5.7
11.2
6.0
3
4
8.2
5.6
5
10.0
9.3
7.9
10.1
7.0
7
8.4
8
7.4
9.0
9
7.0
9.2
6.0
8.1
10
10.0
8.3
8.6
11
12
8.1
13
10.5
10.4
5.5
10.0
7.0
11.2
14
15

Transcribed Image Text:Twinned drill holes. A traditional method of verifying
mineralization grades in mining is to drill twinned holes,
i.e., the drilling of a new hole, or “twin," next to an ear-
lier drill hole. The use of twinned drill holes was investi-
gated in Exploration and Mining Geology (Vol. 18, 2009).
Geologists use data collected at both holes to estimate
the total amount of heavy minerals (THM) present at
the drilling site. The data in the following table (based
on information provided in the journal article) represent
THM percentages for a sample of 15 twinned holes drilled
at a diamond mine in Africa. The geologists want to know
if there is any evidence of a difference in the true THM
means of all original holes and their twin holes drilled at
the mine.
a. Explain why the data should be analyzed as paired
differences.
b. Compute the difference between the “Ist Hole" and
"2nd Hole" measurements for each drilling location.
c. Find the mean and standard deviation of the differ-
ences, part b.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Instruction : "d and e"
The Difference table is :
| 1st Hole | 2nd Hole | Difference = 1st Hole - 2nd Hole | |
| 5.5 | 5.7 | -0.2 | |
| 11 | 11.2 | -0.2 | |
| 5.9 | 6 | -0.1 | |
| 8.2 | 5.6 | 2.6 | |
| 10 | 9.3 | 0.7 | |
| 7.9 | 7 | 0.9 | |
| 10.1 | 8.4 | 1.7 | |
| 7.4 | 9 | -1.6 | |
| 7 | 6 | 1 | |
| 9.2 | 8.1 | 1.1 | |
| 8.3 | 10 | -1.7 | |
| 8.6 | 8.1 | 0.5 | |
| 10.5 | 10.4 | 0.1 | |
| 5.5 | 7 | -1.5 | |
| 10 | 11.2 | -1.2 | |
| n | 15 | 15 | 15 |
Now, we will calculate the mean and standard deviations of the difference Value :
| Difference = 1st Hole - 2nd Hole |
| -0.2 |
| -0.2 |
| -0.1 |
| 2.6 |
| 0.7 |
| 0.9 |
| 1.7 |
| -1.6 |
| 1 |
| 1.1 |
| -1.7 |
| 0.5 |
| 0.1 |
| -1.5 |
| -1.2 |
Sum = Σx = 2.1
Mean =
Standard Deviation : sd
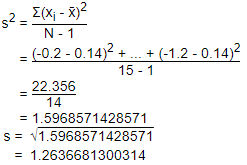
sd = 1.263
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman