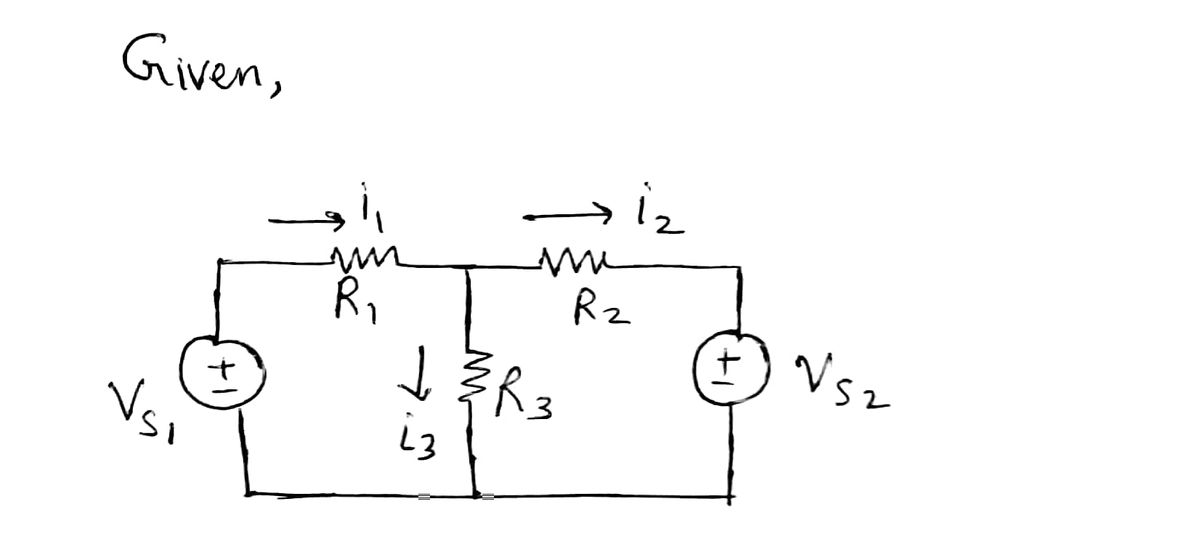
d two independent voltage sources, as shown in Figure 1. et 11, 12, 13 represent the currents that flow through the re- stors, R₁, R2, R3 represent their resistances, and vs1, Us2 present the voltages at the voltage sources. (a) Using Ohm's and Kirchhoff's laws, express 11, 12, 13 as functions of R₁, R2, R3, US1, Us2. Write your result in the form of y= Ax, where y = [i i2 i3] and x = [Us1 Us2] T. (b) Let R₁ = R₂ = R3 = 1. Is it possible for two distinct pairs of voltages, Us1, Us2 and v1, 2, to : L Vsl R₁ R3 Figure 1 R₂ Vs2
d two independent voltage sources, as shown in Figure 1. et 11, 12, 13 represent the currents that flow through the re- stors, R₁, R2, R3 represent their resistances, and vs1, Us2 present the voltages at the voltage sources. (a) Using Ohm's and Kirchhoff's laws, express 11, 12, 13 as functions of R₁, R2, R3, US1, Us2. Write your result in the form of y= Ax, where y = [i i2 i3] and x = [Us1 Us2] T. (b) Let R₁ = R₂ = R3 = 1. Is it possible for two distinct pairs of voltages, Us1, Us2 and v1, 2, to : L Vsl R₁ R3 Figure 1 R₂ Vs2
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question
Parts A and B
![Consider a linear static circuit consisting of three resistors
and two independent voltage sources, as shown in Figure 1.
Let 11, 12, 13 represent the currents that flow through the re-
sistors, R₁, R2, R3 represent their resistances, and Us1, Us2
represent the voltages at the voltage sources.
(a) Using Ohm's and Kirchhoff's laws, express
11, 12, 13 as functions of R₁, R2, R3, Usl, Us2.
Write your result in the form of y = Ax, where
y = [1 12 13] and x = [vs1
US2] T.
(b) Let R₁
=
R₂ R3 = 1. Is it possible for two
distinct pairs of voltages, Us1, Us2 and v1, 2, to
produce the same currents i1, 12, 13? Why?
=
Vsl
+
W
R₁
M
R₂
R3
Figure 1
Vs2
(c) Let R₁ = R₂ = R3 = 1. Find Us1, Us2 that yield i₁ = 1, 12 = -4, 13 = 5. Is this possible? Why?
(d) Repeat (c) with i₁ = 2, 12 = 0, i3 = -3. What is different this time?
(e) Suppose, for safety reasons, the currents must satisfy 1 ≤ i ≤ 2, 1 ≤ i ≤ 2, and 0 ≤ i3 ≤ 1. On
a two-dimensional plane, sketch the set of all voltages Us1, Us2 that ensure these conditions.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F1df17bca-13fe-4084-844e-d71409422be9%2Fc31db936-b016-46a2-a392-1f7b42cdfeb5%2Fpxy0h3_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a linear static circuit consisting of three resistors
and two independent voltage sources, as shown in Figure 1.
Let 11, 12, 13 represent the currents that flow through the re-
sistors, R₁, R2, R3 represent their resistances, and Us1, Us2
represent the voltages at the voltage sources.
(a) Using Ohm's and Kirchhoff's laws, express
11, 12, 13 as functions of R₁, R2, R3, Usl, Us2.
Write your result in the form of y = Ax, where
y = [1 12 13] and x = [vs1
US2] T.
(b) Let R₁
=
R₂ R3 = 1. Is it possible for two
distinct pairs of voltages, Us1, Us2 and v1, 2, to
produce the same currents i1, 12, 13? Why?
=
Vsl
+
W
R₁
M
R₂
R3
Figure 1
Vs2
(c) Let R₁ = R₂ = R3 = 1. Find Us1, Us2 that yield i₁ = 1, 12 = -4, 13 = 5. Is this possible? Why?
(d) Repeat (c) with i₁ = 2, 12 = 0, i3 = -3. What is different this time?
(e) Suppose, for safety reasons, the currents must satisfy 1 ≤ i ≤ 2, 1 ≤ i ≤ 2, and 0 ≤ i3 ≤ 1. On
a two-dimensional plane, sketch the set of all voltages Us1, Us2 that ensure these conditions.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,