cos(x? – x) = x*
Optimization
Optimization comes from the same root as "optimal". "Optimal" means the highest. When you do the optimization process, that is when you are "making it best" to maximize everything and to achieve optimal results, a set of parameters is the base for the selection of the best element for a given system.
Integration
Integration means to sum the things. In mathematics, it is the branch of Calculus which is used to find the area under the curve. The operation subtraction is the inverse of addition, division is the inverse of multiplication. In the same way, integration and differentiation are inverse operators. Differential equations give a relation between a function and its derivative.
Application of Integration
In mathematics, the process of integration is used to compute complex area related problems. With the application of integration, solving area related problems, whether they are a curve, or a curve between lines, can be done easily.
Volume
In mathematics, we describe the term volume as a quantity that can express the total space that an object occupies at any point in time. Usually, volumes can only be calculated for 3-dimensional objects. By 3-dimensional or 3D objects, we mean objects that have length, breadth, and height (or depth).
Area
Area refers to the amount of space a figure encloses and the number of square units that cover a shape. It is two-dimensional and is measured in square units.
Use Newton’s method to find all the roots of the
equation correct to eight decimal places. Start by drawing a
graph to find initial approximations.

Newton's method: This method is also known as Newton Raphson method and it is a technique used to
find the approximation of the root of the function.
It is given that . Rewriting it, we get, . Let us define a function
such that . Then, the derivative of is .
The graph of the function is given below:
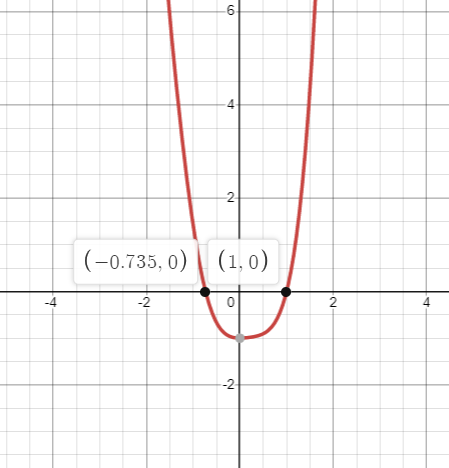
Since the curve intersects the x-axis at two points, there are two roots of the equation . Let
us consider the initial approximations and .
First, we will use the initial approximation .
First iteration:
We have and . So we get,
Hence, .
Second iteration:
We have and . So we get,
Hence, .
Third iteration:
We have and . So we get,
Hence, .
Fourth iteration:
We have and . So we get,
Hence, .
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 1 images









