Computer, the correlation coefficient, using the following data. (Round to three decimal places.) X y 8 0 1 9 53 |7 1 36 46
Computer, the correlation coefficient, using the following data. (Round to three decimal places.) X y 8 0 1 9 53 |7 1 36 46
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
![**Compute \( r \), the correlation coefficient, using the following data:**
\[
\begin{array}{c|cccccc}
x & 8 & 1 & 5 & 7 & 3 & 4 \\
\hline
y & 0 & 9 & 3 & 1 & 6 & 6 \\
\end{array}
\]
**\( r = \) \([\text{Round to three decimal places.}]\)**
---
**Explanation:**
This problem requires calculating the Pearson correlation coefficient \( r \) using the paired data points \((x, y)\). The data points are organized into two rows, with the first row representing the variable \( x \) and the second row the variable \( y \). Calculating \( r \) involves determining how strongly and in what direction the two variables are linearly related. The correlation coefficient \( r \) ranges from -1 to 1, with values close to -1 indicating a strong negative linear relationship, values close to 1 indicating a strong positive linear relationship, and values around 0 indicating no linear correlation.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F58402a47-f1ff-47ea-9009-84135bb68162%2F04bcfbc3-d51e-4c54-956f-ffbd04b32704%2Fbkd05n4_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Compute \( r \), the correlation coefficient, using the following data:**
\[
\begin{array}{c|cccccc}
x & 8 & 1 & 5 & 7 & 3 & 4 \\
\hline
y & 0 & 9 & 3 & 1 & 6 & 6 \\
\end{array}
\]
**\( r = \) \([\text{Round to three decimal places.}]\)**
---
**Explanation:**
This problem requires calculating the Pearson correlation coefficient \( r \) using the paired data points \((x, y)\). The data points are organized into two rows, with the first row representing the variable \( x \) and the second row the variable \( y \). Calculating \( r \) involves determining how strongly and in what direction the two variables are linearly related. The correlation coefficient \( r \) ranges from -1 to 1, with values close to -1 indicating a strong negative linear relationship, values close to 1 indicating a strong positive linear relationship, and values around 0 indicating no linear correlation.
Expert Solution
Step 1
We have to solve given problem:
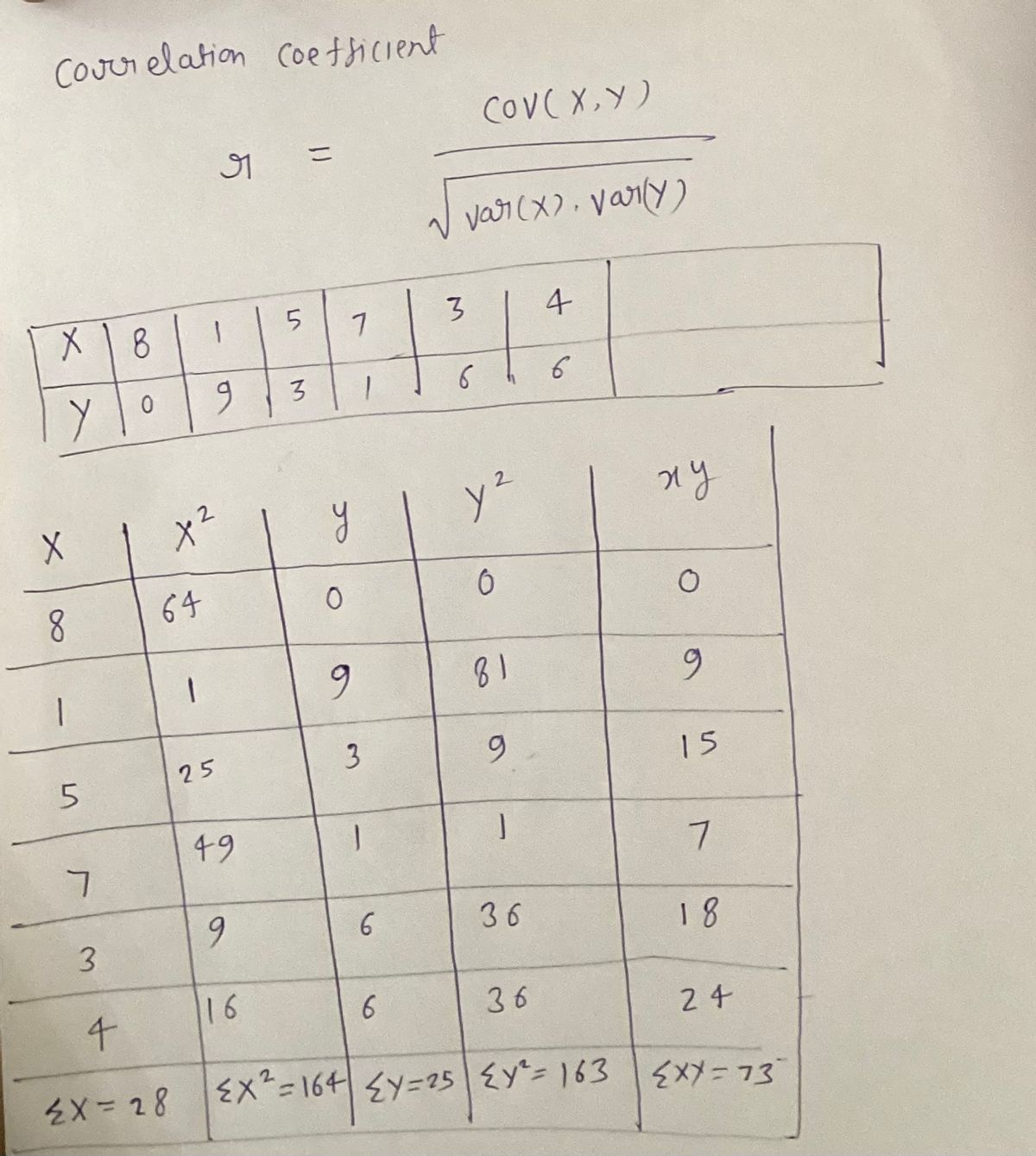
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

