Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
100%
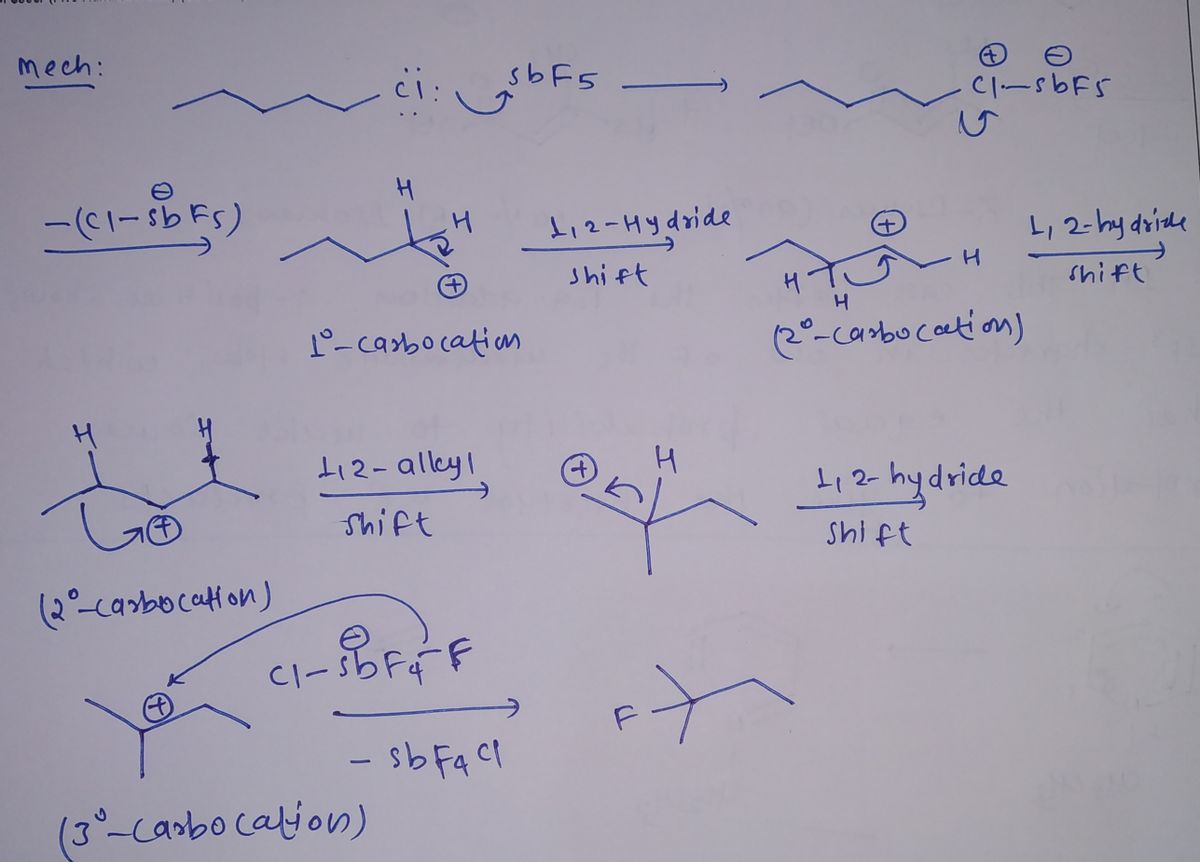
What is the mechanism?

Transcribed Image Text:The image shows a chemical reaction diagram.
**Left Side:**
- A skeletal formula of an organic compound is depicted. The structure features a linear alkane chain that culminates in a chlorine atom (Cl).
**Center:**
- A reaction arrow indicates the direction of the reaction. Above the arrow, the reagent "SbF₅" is noted, which stands for antimony pentafluoride.
**Right Side:**
- Another skeletal formula with a new structure is illustrated. This structure appears as a branched alkane with a fluorine atom (F) attached to the branch.
**Explanation:**
This diagram represents the transformation of a chloroalkane into a fluoroalkane using SbF₅ as a reagent. The chlorine atom is replaced by a fluorine atom, resulting in a branched structure in the product. This kind of reaction showcases a halogen exchange facilitated by a strong Lewis acid like antimony pentafluoride.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY