
Strong bases tend to ionize completely whereas weak bases tend to ionize partially. The weak base's dissociation constant always remains very small compared to strong base due to its partial dissociation/ionization.
Given
The initial concentration of methylamine is 0.092 M.
The concentration of methylammonium chloride is 0.10 M.
The chemical equation for dissociation/ionization of methylamine in an aqueous solution is shown below.
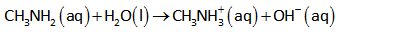
The ICE table for the above reaction is shown below.
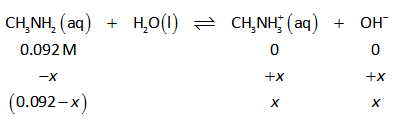
The hydroxide ions concentration is calculated by the dissociation constant expression as shown below.
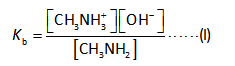
Here,
The dissociation constant is “Kb”.
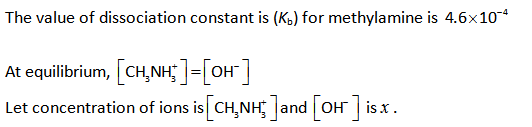
Substitute the known values in the equation (I).
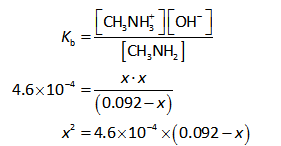
Since methylamine is a weak base and it dissociates partially in aqueous solution. And the dissociation constant of methylamine is very small and thus, (0.092-x) can be approximated to 0.092.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 10 images









