Given the chart of bond energies, calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction below. Show all work to receive full credit. Average Bond Energies (kJ/mol) H-H H-C1 H-F 436 kJ/mol С-Н 413 kJ/mol С-С 614 kJ/mol 431 kJ/mol СС 348 kJ/mol C=C 839 kJ/mol 567 kJ/mol C-N 293 kJ/mol C=0 799 kJ/mol N-H 391 kJ/mol C-O 358 kJ/mol O=0 495 kJ/mol N-O 201 kJ/mol C-F 485 kJ/mol C=0 1072 kJ/mol 463 kJ/mol 146 kJ/mol 155 kJ/mol C-CI C-S C=N N=N O-H 328 kJ/mol 615 kJ/mol 0-0 259 kJ/mol 418 kJ/mol CI-CI 242 kJ/mol 941 kJ/mol 891 kJ/mol F-F N=N C=N N=Ñ + -7H-N-H H-H H-H H-N-H
Types of Chemical Bonds
The attractive force which has the ability of holding various constituent elements like atoms, ions, molecules, etc. together in different chemical species is termed as a chemical bond. Chemical compounds are dependent on the strength of chemical bonds between its constituents. Stronger the chemical bond, more will be the stability in the chemical compounds. Hence, it can be said that bonding defines the stability of chemical compounds.
Polarizability In Organic Chemistry
Polarizability refers to the ability of an atom/molecule to distort the electron cloud of neighboring species towards itself and the process of distortion of electron cloud is known as polarization.
Coordinate Covalent Bonds
A coordinate covalent bond is also known as a dative bond, which is a type of covalent bond. It is formed between two atoms, where the two electrons required to form the bond come from the same atom resulting in a semi-polar bond. The study of coordinate covalent bond or dative bond is important to know about the special type of bonding that leads to different properties. Since covalent compounds are non-polar whereas coordinate bonds results always in polar compounds due to charge separation.
How do I solve?

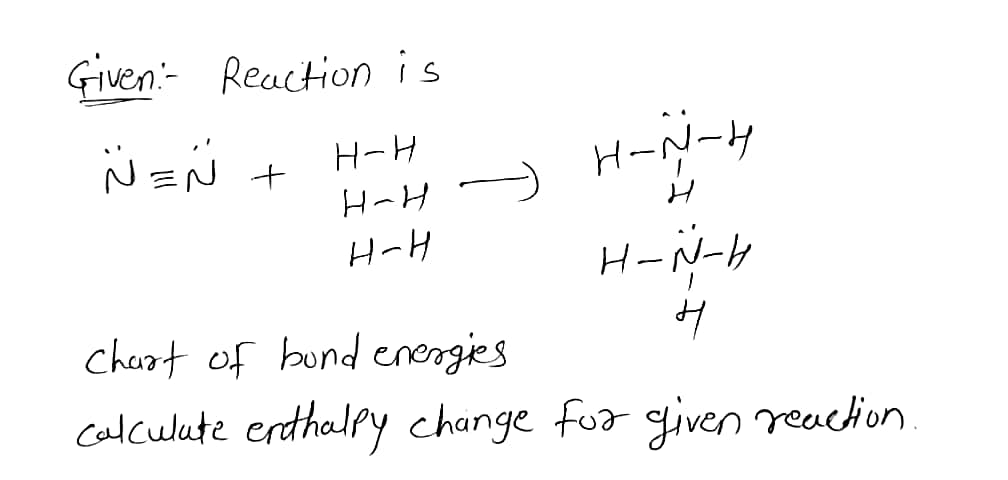
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









