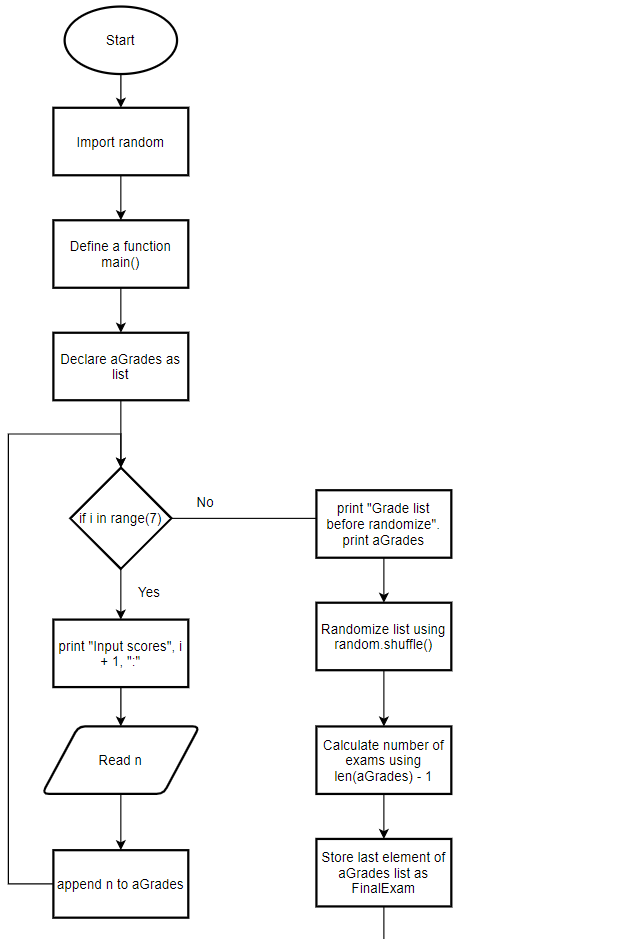
*Can you produce a flowchart for this code. import random def main(): # main function definition aGrades=[] # empty list to store Grades for i in range(7): # loop to read 7 inputs print("Input scores ",i+1," : ", end="") # a message to enter grade n=int(input()) # input grade aGrades.append(n) # add grade into list print("Grade list before randomize: ",aGrades) # print list random.shuffle(aGrades) # randomize list numExams=len(aGrades)-1 # compute numExams FinalExam=aGrades[-1] # store final grade TotalPoints=sum(aGrades)-aGrades[-1] # compute TotalPoints TestAverage=TotalPoints/numExams # compute TestAverage FinalAverage=TestAverage*.6 + FinalExam*.4 # compute FinalAverage print("Grade list after randomize is: ",aGrades) # print list print("Test Average = %.2f"%TestAverage) # print test average print("Final Average = %.2f "%FinalAverage) # print final average main() # calling main function
Types of Loop
Loops are the elements of programming in which a part of code is repeated a particular number of times. Loop executes the series of statements many times till the conditional statement becomes false.
Loops
Any task which is repeated more than one time is called a loop. Basically, loops can be divided into three types as while, do-while and for loop. There are so many programming languages like C, C++, JAVA, PYTHON, and many more where looping statements can be used for repetitive execution.
While Loop
Loop is a feature in the programming language. It helps us to execute a set of instructions regularly. The block of code executes until some conditions provided within that Loop are true.
*Can you produce a flowchart for this code.
import random
def main(): # main function definition
aGrades=[] # empty list to store Grades
for i in range(7): # loop to read 7 inputs
print("Input scores ",i+1," : ", end="") # a message to enter grade
n=int(input()) # input grade
aGrades.append(n) # add grade into list
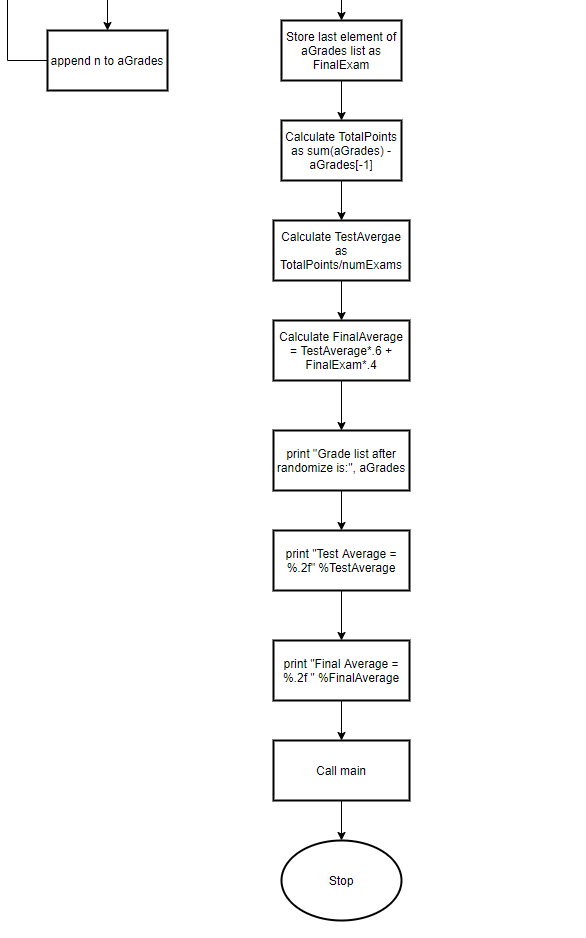
print("Grade list before randomize: ",aGrades) # print list
random.shuffle(aGrades) # randomize list
numExams=len(aGrades)-1 # compute numExams
FinalExam=aGrades[-1] # store final grade
TotalPoints=sum(aGrades)-aGrades[-1] # compute TotalPoints
TestAverage=TotalPoints/numExams # compute TestAverage
FinalAverage=TestAverage*.6 + FinalExam*.4 # compute FinalAverage
print("Grade list after randomize is: ",aGrades) # print list
print("Test Average = %.2f"%TestAverage) # print test average
print("Final Average = %.2f "%FinalAverage) # print final average
main() # calling main function
The following is the flowchart for the above code:
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









