1. You may begin this part of the experiment while the electrolysis is progressing. These studies be interrupted when the electrolysis is completed. 2. After you have read all of the instructions, determine the anodes, cathodes, and voltages of the following voltaic cells: Cu²+ | Cu and Pb²+ | Pb Cu²+ | Cu and Fe²+ | Fe Cu² | Cu and Fe*, Fe² | Pt (or graphite) Zn²+ Zn and Pb²+|Pb Zn²+ Zn and Fe²+ | Fe a. b. C. d. e. f. Zn²+ | Zn and Fe³+, Fe²+ | Pt (or graphite) g. Fe| Fe and Fe³+, Fe² | Pt (or graphite) ight 2017 Cengage Leaming. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, sesed, or delicated, in whole or in pat. Due to electronic sights, see this party content may be suppressed from the eBook ander Chapters) niew has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall leaming experience. Cengage Leaming reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions requi you are using a salt bridge, also include Pb²+ | Pb and Fe²+ | Fe Pb² | Pb and Fe, Fe² | Pt (or graphite) Experiment 19B
1. Use the identities of the anode and cathode to give the overall cell reaction for each voltaic cell. 2. b. Use the Nernst equation, where necessary, to calculate E°cell for each overall cell reaction.


Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Can the ones with graphite be done with graphite instead. . Use the identities of the anode and cathode to give the overall cell reaction for each voltaic cell.
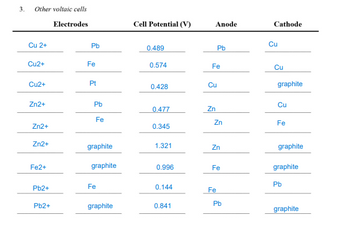
Show that your experimental results are in agreement with the following statements about reactions that occur outside of a voltaic cell. a. Zn will reduce Cu2+ ions, but Zn2+ ions are not reduced by Cu. b. Fe2+ ions are not oxidized by Zn2+ ions. c. When an iron nail is inserted into a solution of Cu2+ ions, metallic copper is deposited on the nail. d. When a piece of lead is inserted into a solution of Zn2+ ions, no reaction occurs. 5. a. Calculate the expected cell potential from the copper concentration cell before the addition of 0.10 M Cu(NO3)2.








