Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
calculate the energy change when an electron in the hydrogen atom transitions from n=3 to n=1

Transcribed Image Text:The image displays an energy level diagram for an electron in an atom. The diagram has three energy levels, each represented by a horizontal line. Each line is labeled with the principal quantum number \( n \) and the corresponding energy \( E \). The energies are expressed in joules (J).
- **Level \( n = 3 \):**
- Energy \( E_3 = -2.42 \times 10^{-19} \) J
- **Level \( n = 2 \):**
- Energy \( E_2 = -5.45 \times 10^{-19} \) J
- **Level \( n = 1 \):**
- Energy \( E_1 = -2.18 \times 10^{-18} \) J
The diagram is used to illustrate the discrete energy levels available to an electron within an atom. As electrons transition between these levels, they absorb or emit energy equal to the difference between the initial and final energy levels. This concept is foundational in understanding atomic structure and spectral lines.
Expert Solution
Step 1
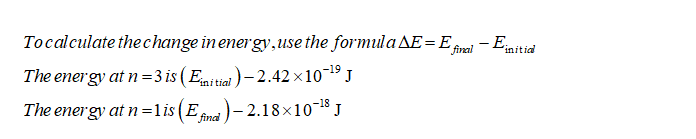
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY