C. On your graph of the short and long-run Phillips Curves from part (A), show the effect that the Canadian recession will have on the U.S. economy. Label your new equilibrium point B. D. Assume that prices and wages are flexible and that U.S. policymakers take no action. What will happen to each of the following as the economy approaches long-run equilibrium? Short-run aggregate supply. Explain. i. ii. Short-run Phillips curve
Answer ONLY parts C and D.

The Phillips curve is a tool that is used to represent the trade-off that economies face between the level of unemployment and the level of inflation in the economy. A lower rate of unemployment can only be achieved if the economy is willing to deal with higher levels of inflation.
Part C
The recession in the Canadian economy will reduce the level of export demand in the US economy. The AD curve shifts down, and there is a lower demand at each and every price level. This causes a downward movement in the SRPC, and there is a lower level of equilibrium inflation and a higher unemployment rate in the short run.
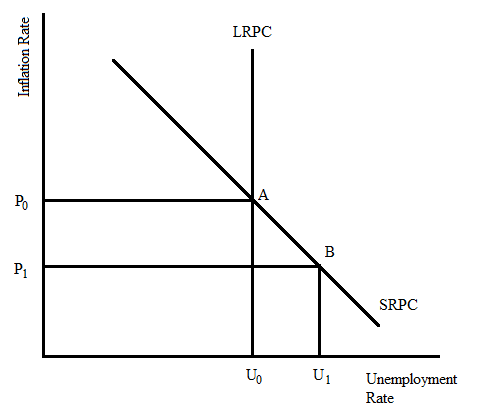
Part D (i)
There will be a movement along the short-run aggregate supply curve as there will be an equilibrium with the lower aggregate demand curve. Since the prices and costs are flexible, there will be no price misperceptions, and the supply remains constant at a lower level of inflation. Under perfect flexibility, the short-run aggregate supply curve is equal to the long-run aggregate supply curve.
Part D (ii)
The short-run Philips curve will shift downwards and settle at the lower level of equilibrium inflation and original unemployment. The equilibrium will be extended from Point B in the graph above to meet the LRPC at a lower inflation rate.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









