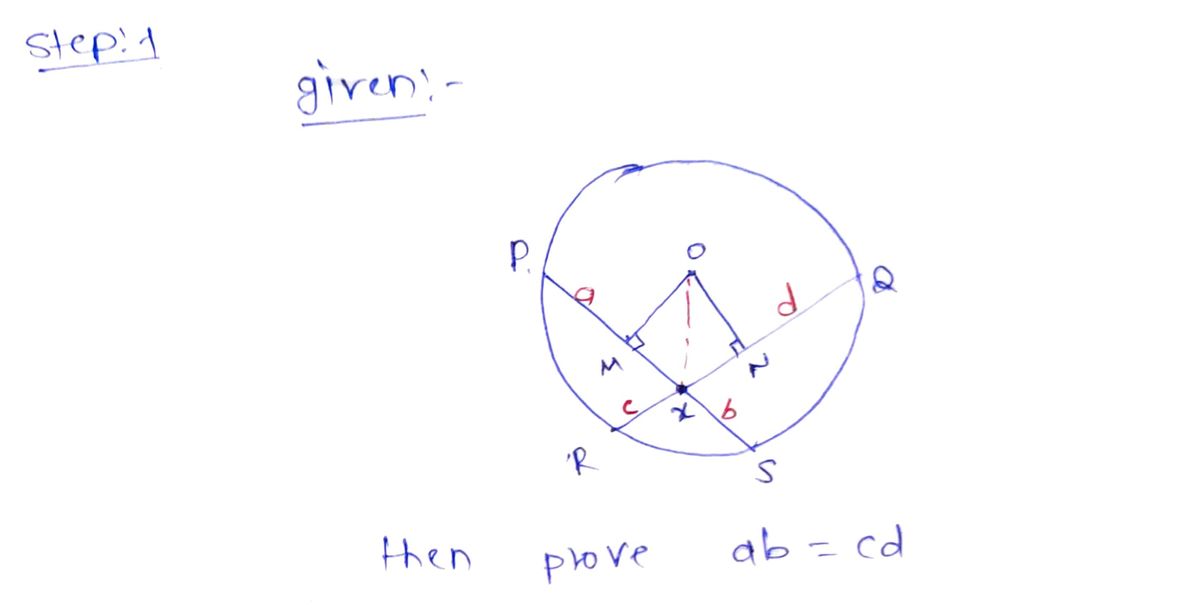
(C) Your students have learned that if two chords intersect within a circle, then the product of the segments of one chord is equal to the product of the segments of the other chord. That is, in the following diagram, ab = cd. Some of your more curious students want to know how that is proven. How do you do it? [Hint: Draw the dotted lines as shown in Figure 5.32, and try to get similar triangles.] R O b Figure 5.32 'S
(C) Your students have learned that if two chords intersect within a circle, then the product of the segments of one chord is equal to the product of the segments of the other chord. That is, in the following diagram, ab = cd. Some of your more curious students want to know how that is proven. How do you do it? [Hint: Draw the dotted lines as shown in Figure 5.32, and try to get similar triangles.] R O b Figure 5.32 'S
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
ChapterP: Preliminary Concepts
SectionP.CT: Test
Problem 1CT
Related questions
Question
![(C) Your students have learned that if two chords intersect within a circle, then the product of the segments of one chord is equal to the product of the segments of the other chord. That is, in the following diagram, \( ab = cd \). Some of your more curious students want to know how that is proven. How do you do it? [Hint: Draw the dotted lines as shown in Figure 5.32, and try to get similar triangles.]
**Figure 5.32 Explanation:**
- The circle contains an intersecting system of chords.
- Chord \( PQ \) is intersected by chord \( RS \) inside the circle at point \( T \).
- The segments of the chords are labeled as follows:
- \( PT = a \)
- \( TQ = b \)
- \( RT = c \)
- \( TS = d \)
- According to the intersecting chords theorem, \( ab = cd \).
To understand this theorem, it is helpful to draw the additional lines connecting \( P \) to \( S \) and \( Q \) to \( R \) as hinted. This creates triangles \( \triangle PTR \), \( \triangle QTS \), \( \triangle QTR \), \( \triangle PTS \), which can help in finding similar triangles and proving the theorem.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F98b6e310-08ba-4e1d-a9bc-704b45d2ce6c%2F4673196e-3a5f-4ed4-bd4d-641a24b28100%2Fybl3rty_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:(C) Your students have learned that if two chords intersect within a circle, then the product of the segments of one chord is equal to the product of the segments of the other chord. That is, in the following diagram, \( ab = cd \). Some of your more curious students want to know how that is proven. How do you do it? [Hint: Draw the dotted lines as shown in Figure 5.32, and try to get similar triangles.]
**Figure 5.32 Explanation:**
- The circle contains an intersecting system of chords.
- Chord \( PQ \) is intersected by chord \( RS \) inside the circle at point \( T \).
- The segments of the chords are labeled as follows:
- \( PT = a \)
- \( TQ = b \)
- \( RT = c \)
- \( TS = d \)
- According to the intersecting chords theorem, \( ab = cd \).
To understand this theorem, it is helpful to draw the additional lines connecting \( P \) to \( S \) and \( Q \) to \( R \) as hinted. This creates triangles \( \triangle PTR \), \( \triangle QTS \), \( \triangle QTR \), \( \triangle PTS \), which can help in finding similar triangles and proving the theorem.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning