C b. 108° с
Trigonometry (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN:9780134217437
Author:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Chapter1: Trigonometric Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RE:
1. Give the measures of the complement and the supplement of an angle measuring 35°.
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:This image shows a triangle labeled with vertices A, B, and C.
- **Angle**: At vertex A, there is a labeled angle of 108°.
- **Sides**:
- The side opposite angle A (between vertices B and C) is labeled as "x."
- The side between vertices A and B is labeled as "c."
- The side between vertices A and C is labeled as "b."
This represents an obtuse triangle since one of its angles is greater than 90°.
![**Problem Statement:**
Use the law of cosines to determine the indicated side \( x \). Assume \( b = 11 \) and \( c = 13 \). Round your answer to one decimal place.
**Explanation:**
The Law of Cosines is a formula used to find the length of a side in any triangle when you know the lengths of the other two sides and the measure of the included angle. It is generally written as:
\[ a^2 = b^2 + c^2 - 2bc \cdot \cos(A) \]
From the given problem:
- Side \( b \) is 11
- Side \( c \) is 13
- \( x \) is the side opposite angle \( A \), which we need to find
To solve for \( x \), we need to know the measure of angle \( A \). If not given, additional information would be needed for a full solution. The result should be rounded to one decimal place.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F410204a0-8764-4473-a9c2-14bad68c17f5%2F59d83439-7a1c-422b-bcfe-5a053bac2e90%2Fqlb3oi9_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
Use the law of cosines to determine the indicated side \( x \). Assume \( b = 11 \) and \( c = 13 \). Round your answer to one decimal place.
**Explanation:**
The Law of Cosines is a formula used to find the length of a side in any triangle when you know the lengths of the other two sides and the measure of the included angle. It is generally written as:
\[ a^2 = b^2 + c^2 - 2bc \cdot \cos(A) \]
From the given problem:
- Side \( b \) is 11
- Side \( c \) is 13
- \( x \) is the side opposite angle \( A \), which we need to find
To solve for \( x \), we need to know the measure of angle \( A \). If not given, additional information would be needed for a full solution. The result should be rounded to one decimal place.
Expert Solution
Step 1
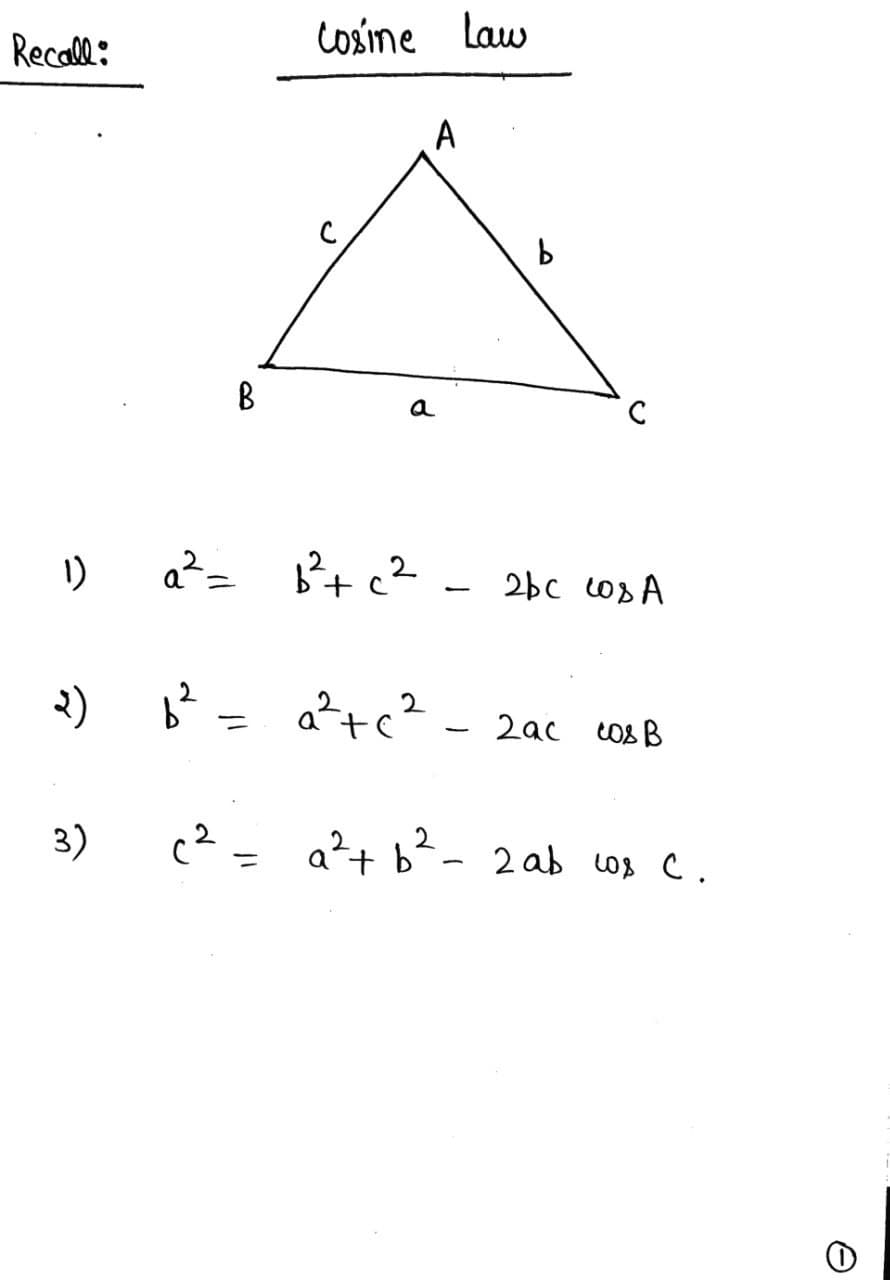
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9780134217437
Author:
Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher:
PEARSON

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9780134217437
Author:
Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher:
PEARSON

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning