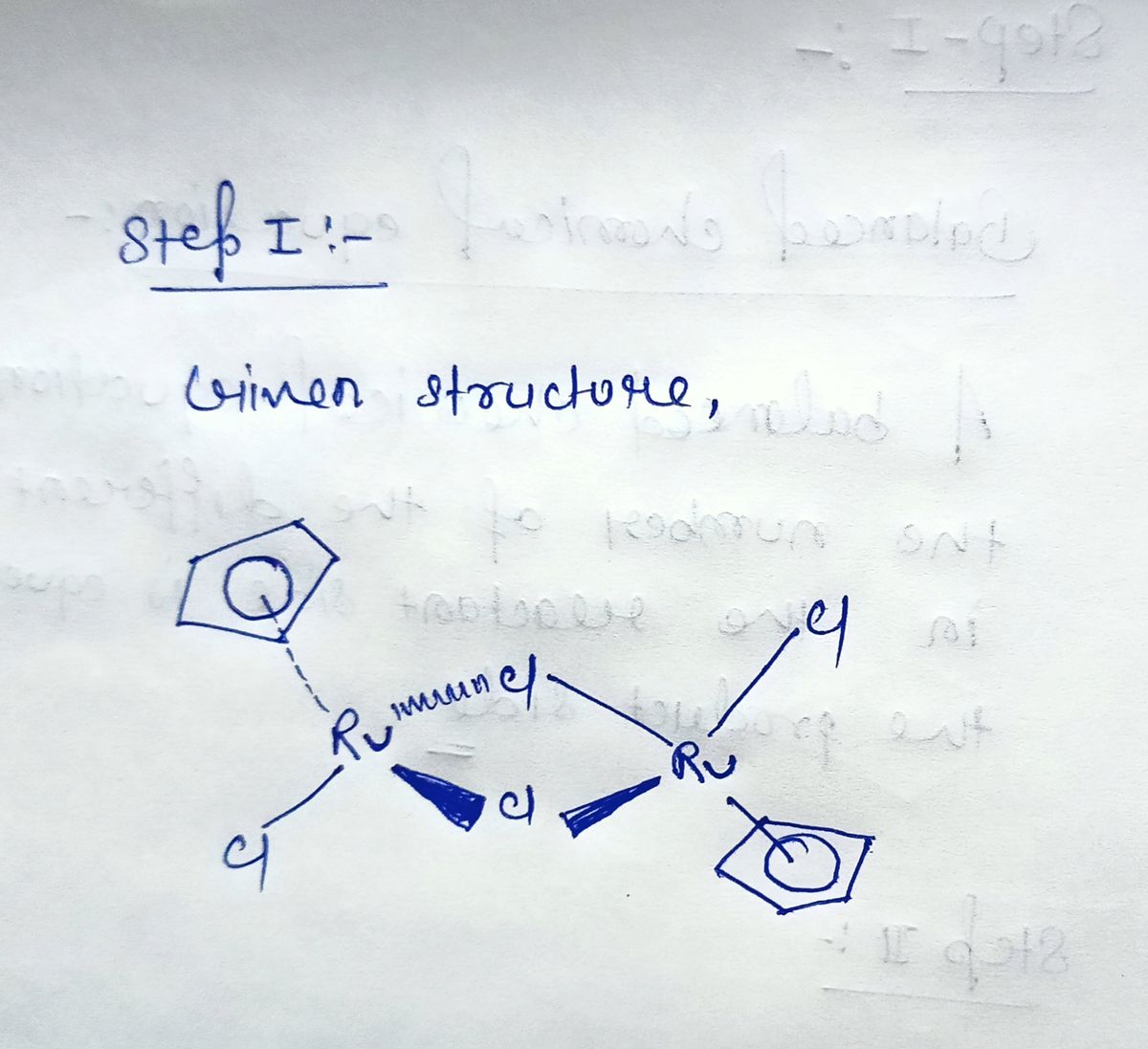
Bridging structures are quite common in coordination compounds. In this kind of structure, the ligand charge is split between the number of metals that it is bonded. For example, if a ligand with charge 2+ is bridging two metals, each metal will “feel” a 1+ charge. What is the oxidation state, and the number of d- electrons for each ruthenium atom in the structure below?
Atomic Structure
The basic structure of an atom is defined as the component-level of atomic structure of an atom. Precisely speaking an atom consists of three major subatomic particles which are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Many theories have been stated for explaining the structure of an atom.
Shape of the D Orbital
Shapes of orbitals are an approximate representation of boundaries in space for finding electrons occupied in that respective orbital. D orbitals are known to have a clover leaf shape or dumbbell inside where electrons can be found.
Bridging structures are quite common in coordination compounds. In this kind of structure, the ligand
charge is split between the number of metals that it is bonded. For example, if a ligand with charge 2+ is
bridging two metals, each metal will “feel” a 1+ charge. What is the oxidation state, and the number of d-
electrons for each ruthenium atom in the structure below?

Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









